Welcome to kashibiology.com. In the previous post we have learned about the role of microbes in Ethanol Production.
This post is based all about the Antibiotics.
What is Antibiotics?
I hope all of you are aware about the antibiotic. In most of the diseases doctors prescribed the antibiotic.
You have also seen the antibiotic in tablet form, capsule form or sometimes in liquid form which is injected by Syringes.
But what is the exact antibiotic? And which type of organisms produce antibiotics? How the discovery of antibiotics was started and how the antibiotics exactly work against pathogenic microbes, all these questions are discussed in detail here.
In the Greek word Anti means against, and Bios means life. Hence antibiotics are the chemicals which work against life.
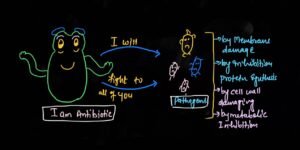
Antibiotics are the chemicals of microbial origin of metabolic processes, which can kill or retard the growth of other microbes without any harmful effects on the host body.
Presently more than 7000 antibiotics have been discovered from different strains of bacteria fungus, lichen and Actinomycetes.
It is very interesting that most of the antibiotics are bacterial in origin and they inhibit the growth or kill other bacterial species.
Another very interesting story behind the antibiotic discovery is that the first antibiotic was not discovered intentionally but it was discovered by chance by Alexander Fleming. He observed that the extract of the fungus Penicillium notatum inhibits the growth of a bacterium called Staphylococcus.
Historical Aspects
The term antibiotic was given by Waksman in 1942.
The first antibiotic was discovered from a fungus Penicillium notatum. It was called Penicillin and it was discovered by a famous biologist Alexander Fleming while working on a bacterial species Staphylococcus.
Much later commercial extraction of antibiotics was done by Chain and Florey.
The same antibiotic was used in the treatment of American Soldiers in World War II.
- In 1945 Biologist- Fleming, Chain and Florey were awarded the Nobel Prize for the discovery of antibiotics.
- In 1941 Waksman and Woodruff discovered and isolated antibiotic Actinomycin.
- In 1942 they also discovered antibiotic Streptothricin.
- In 1943 Waksman and Albert discovered antibiotic Streptomycin.
- In 1947 Chloromycetin was isolated by Burkholder.
Most antibiotics directly kill or inhibit the growth of disease causing microbes by disturbing the metabolic processes of the pathogenic microorganism which are essential for the survival of such pathogenic organisms.
Types of Antibiotics
Antibiotics can be classified on the basis of their mode of action, their mode of origin and their working spectrum.
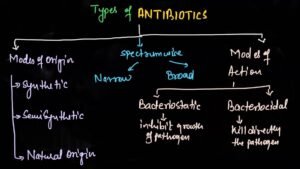
1: On the basis of mode of action-
According to this antibiotic is of two types
Bactericidal antibiotics-
That is antibiotics which directly kill disease causing pathogens or bacteria.
Bacteriostatic antibiotics-
Bacteriostatic antibiotics are those which inhibit the growth of bacteria.
2: On the basis their origin-
On the basis of source of source of antibiotic it is of following types
Derived or natural antibiotics-
It is directly obtained from source microorganisms. It is produced by a natural metabolic process and obtained as an extract, which after purification and testing is used for treatment.
Semi synthetic antibiotics-
These are also of natural microbial origin but to increase their effectiveness. There is some chemical modification done in their chemical structure. Therefore their effectiveness has increased.
Synthetic antibiotics-
These are purely prepared in the laboratory by the use of different types of raw material.
3: On the basis of Range
Antibiotic can also be classified into broad spectrum or narrow spectrum
Broad spectrum antibiotics-
Broad spectrum antibiotics kill or destroy a number of disease causing pathogens without any specific structure or their cell wall composition of pathogenic microbes.
Narrow spectrum antibiotics-
These are the specific antibiotics, which are specifically designed and worked against of particular pathogenic microbes.
Source Organisms for Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the specific chemicals, originate in metabolic processes. They are obtained from different types of microbes which belong to different groups such as Bacteria, Lichen and Fungi.
For example- Streptomyces griseus produces more than 41 antibiotics while Bacillus subtilis producers some of the 60 antibiotics.
The lichen Usnea and Cladonia produces antibiotic usnic acid
In bacteria Pseudomonas produces 30% of total antibiotic types and Bacillus covers the 70% of all antibiotic productions.
Fungus also produces different types of antibiotics such as the first antibiotic penicillin is obtained from Penicillium notatum.
Some other antibiotics such as cephalosporin obtained from sea Fungi Cephalosporium acremonium
Clitocybine obtained from Fungi Clitocybine gigantea
Clavacin obtained from Aspergillus clavatus
Citrinin obtained from Aspergillus clavatus
Similarly most of the famous antibiotics such as streptomycin, Chloramphenicol, tetracycline Terramycin and erythromycin obtain form Actinomycetes or Streptomyces.
Some other antibiotic producing Actinomycetes species are-
Streptosporangium
Micromonospora
Nicardina
Actinoplanes
Some antibiotics are semisynthetic such as Ampicillin, Oxocillin.
Characteristics of an ideal Antibiotic
An ideal antibiotic should has following characteristics-
- It should be harmless to Host body
- Minimum or no side effect
- It has no harm to other useful microbes inside the body
- It has the ability to destroy specific pathogen
- It should be effective against most of the strain of pathogen
- It should be quickly absorbed and start quick action.
- It should destroy targeted pathogens without working against non-targeted host cells.
Mode of action of Antibiotics
Different antibiotics perform different actions and follow different pathways to destroy the disease causing pathogen.
Some antibiotics work in inhibition of the process of protein synthesis at different levels.
Most of the antibiotic disturbs biochemical or metabolic processes of pathogens.
Therefore pathogens will die or their growth is restricted inside the body.
Some of the antibiotics action and their names are as follows
Polymyxin, Amphotericin disturb the plasma membrane repair and synthesis
Penicillin & Cephalosporin interfere cell wall synthesis of bacteria.
Erythromycin inhibits the 50s ribosomal subunit of the pathogenic bacteria therefore protein synthesis disturb.
Streptomycin and Neomycin antibiotics bind to 30s ribosomal small subunits. Therefore Protein synthesis disturbed
Tetracycline binds with the t-RNA therefore inhibits its action resulting in Protein synthesis inhibited.
Chloramphenicol involved in Inhibition of translation process and resulting Protein synthesis disturbed.
Diseases in which Antibiotics are used
Most antibiotics are used in the treatment of pathogenic diseases.
some common antibiotic and their targeted diseases are as follows-
Penicillin in tonsillitis, sore throat, and some pneumonia types
- Streptomycin in meningitis, pneumonia and tuberculosis
- Chloromycetin in whooping cough and urinary infection
- Chloramphenicol in typhoid, typhus, whooping cough and pneumonia
- Tetracycline in viral, pneumonia, whooping cough.
- Viridin work against Fungal infection
- Terramycin prevents again intestinal and urinary infection
- Erythromycin in typhoid, common pneumonia, whooping cough and diphtheria.
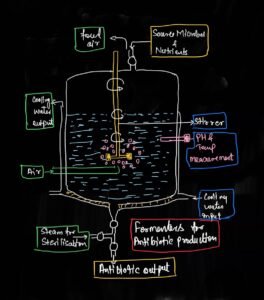
Application of Antibiotics
The most important use of antibiotic is the treatment of different type of pathogenic diseases
Antibiotic also used as preservative in pasteurized and canned food
They are also used as feed supplements for poultry birds.
Antibiotics are also used as marker genes during the gene cloning in plasmid. Antibiotic resistance genes in the plasmid help in the selection of recombinants from non recombinants.
Conclusion
In this post we have learn about the antibiotic, their history of discovery, important contribution of biologists in the discovery of antibiotic, types of antibiotic, action antibiotic and application antibiotics
Hope you will understand what exactly the antibiotic is not in very detail but conceptually.
If you have any suggestion or found any mistake in the post please update us by comment.
Thanks for reading this post.