Welcome to kashibiology. In the previous post we have already discussed the Historical aspects and the different discoveries to identify the light reaction pathway and dark reaction pathway of photosynthesis.
In addition to the above we have also learnt, what are the different important contributions of biologists in the discovery of overall process and the product formation in photosynthesis.
In this post we shall deal the following Questions-
definition of photosynthesis.
Types of photosynthesis.
What are the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
What is site photosynthesis?
What is the compartmentalization in chloroplast for different reaction of photosynthesis?
And also understand the structure of chloroplast.
Definition of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a biochemical or physicochemical process by which plant use light energy to drive the synthesis of organic compounds or carbohydrates (glucose) in a special type of plastid called chloroplast by using carbon dioxide gas and water molecules.
Photosynthesis is the primary and ultimate basis of life on earth, because it is the fundamental source of food on earth as well as releasing oxygen gas as a byproduct in the atmosphere.
In the formation of one Glucose molecule there is need of 6 molecules of carbon dioxide gas and 12 molecules of water.
In oxygenic photosynthesis oxygen is released while in Anoxygenic photosynthesis or nonoxygenic photosynthesis instead of oxygen gas, sulphur gas is released.
Types of photosynthesis-
On the basis of release of oxygen in the process of photosynthesis, It is of two types- oxygenic photosynthesis and Anoxygenic photosynthesis.
Oxygenic photosynthesis-
In this process oxygen is evolved and Water used as a reactant after breaking of water molecules in the presence of light oxygen is released.
This process takes place in the entire oxygenic photosynthesis organism such as-
All plants, algae, euglena and photosynthetic prokaryotes such as blue green algae or Cyanobacteria.
I want to mention one important point here, which is that BGA (blue green algae) or Cyanobacteria is the first oxygenic photosynthetic organisms that evolved 350 million years ago.
In Oxygenic photosynthesis, water molecules act as a hydrogen ion and electron donor.
Anoxygenic photosynthesis-

In this process there is no evolution of Oxygen gas Instead of sulphur gas. Here the hydrogen sulphide gas used at the place of water molecule.
Hydrogen sulfide gas acts as the hydrogen and electron donor in Anoxygenic photosynthesis process.
This type of Anoxygenic photosynthesis is performed by the many prokaryotic cells. Such as-
Green sulphur bacteria Chlorobium
Green non sulphur bacteria Chloroflexus
Purple sulphur bacteria Chromatium
Purple non sulphur bacteria Rhodospirillum, Rhodopseudomonas etc.
Requirements of photosynthesis-
The process of photosynthesis requires two inorganic chemicals. One obtained in the gaseous stage (carbon dioxide) and another obtained in the liquid stage (water molecules) from the environment.
The other requirement is a presence of Sunlight which is the source of energy and chloroplast which is the site of photosynthesis.
In prokaryotic organisms, where the chloroplast does not exist but membranous or thylakoid like structures are present where photosynthesis takes place.
Carbon dioxide-
Terrestrial plants obtain carbon dioxide gas from the atmosphere through the stomatal pore by gaseous exchange. Some amount of carbon dioxide also obtained as carbonates from the soil.
In the case of aquatic plants for hydrophytes carbon dioxide obtained from the aquatic environment as bicarbonate and plants absorb it as by their general body surface.
What exactly happens with carbon dioxide molecules in the photosynthesis process?
Actually, in the process of photosynthesis carbon dioxide is used in the dark reaction to reduce glucose. There are 6 molecules required to formation of one molecule of glucose.
Water-
Rain water is the main source for land plants but most of the rainwater flows to nearby water bodies as surface Flow and some of the rain water is passed to as the underground water.
Very little water remains in the soil which is used by the plant. The water used by the plant from the soil is called capillary water.
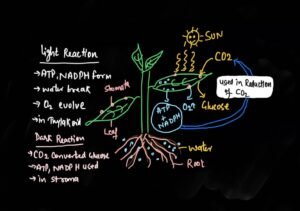
In the process of photosynthesis water is oxidized to produce Oxygen gas as a by-product.
As well as hydrogen ions and electrons are also released during photolysis of water, which are used in the light reaction process to produce assimilatory power or energy rich chemical molecules, namely ATP and NADPH.
There are 18 ATP and 12 NADPH molecules forms after oxidation of 12 molecules of water in light reaction (only in noncyclic Photophosphorylation not in cyclic Photophosphorylation)
Water is absorbed by the root hair cell and then from the root it is transported to upward direction by special conducting tissue called xylem.
Light-
Light is the visible part of electromagnetic radiation. These are a form of energy. photosynthesis occurs in different ranges of wavelength of light, commonly called PAR (photosynthetic active radiation).
PAR (photosynthetic active radiation)-
Part of the light spectrum used in photosynthesis is called PAR. The value of PAR wavelength ranges in between 400 to 700 nm (nanometers).
The blue and red regions of the light spectrum are the most effective in photosynthesis. Green light is least effective.
plants preferred red light in photosynthesis because blue light carries more energy due to its short wavelength (400 nm) while right red light has less energy due to its high (red spectrum-680 nm, far red-700 nm) wavelength.
Chloroplast-The site of Photosynthesis
In higher plants Chloroplast present in the photosynthetic cell or Mesophyll cell which are present in Leaf.
Mesophyll cell is of two types one is palisade Mesophyll while the other is spongy Mesophyll cell.
Palisades Mesophyll cells are tall pillar-like cells and are compactly arranged. They contain a large number of chloroplasts.
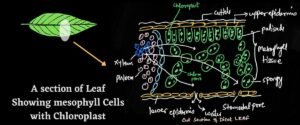
The arrangement of chloroplast in the Mesophyll cells in such a manner to absorb maximum incident of sunlight.
Mesophyll cell located towards the upper surface of Leaves while spongy Mesophyll cell located towards lower surface of leaf.
We often see that the upper surface of the leaf is generally seen dark green in colour as compared to the lower surface of the leaf.
Chloroplast is the membrane bound cell organelle found in all the eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms as well as in some mixotrophic organisms such as Euglena.
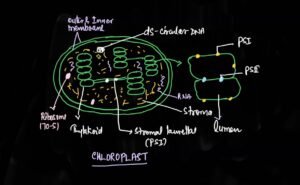
Inside the chloroplast there is clear cut labor of division seen. The membranous coins like structure are called thylakoid and the group of thylakoid is called granum.
Membranous part of the thylakoid contains photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll and carotenoids etc.
It is the site of light reaction where water is broken down and oxygen is evolved as well as the process of phosphorylation take place.
Photosystem or Pigment System-
The photosynthetic pigments are organized to form a photosystem which is the structural and functional unit of light reaction or photophosphorylation reaction.
There are two types of photosystem present in thylakoid membrane namely photosystem I and photosystem II.
Actually their name is derived from their sequence of discovery not related to their sequence of functions.
The photosystem-I located predominantly in an unstacked region or non appressed region of thylakoid. while photosystem-II is dominantly located in the stacked or appressed region of thylakoid as shown in the given figure.
RuBisCO Enzyme-
The Matrix part of chloroplast is called stroma which is the site of carbon dioxide reduction after this formation of glucose takes place.
A very important enzyme RuBisCO (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase) is present in matrix or stroma. It is the most abundant enzyme on the earth.
RuBisCO is the main Enzyme of dark reaction and catalyzed the first step of reactions of C3 cycle.
RuBisCO shows both oxygenase and carboxylase activity. Both the activity related to the relative concentration of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
If the concentration of oxygen increases at the enzymatic site then RuBisCO performs oxygenase activity.
In photorespiration or C2 cycle RuBisCO shows oxygenase activity. Therefore instead of fixation of carbon dioxide there is loss of carbon dioxide.
In photorespiration there is neither synthesis of glucose nor evolution of oxygen rather than use of ATP. Hence photorespiration is considered as a wasteful process.
Conclusion-
Hope after reading this post you will be able to understand types of photosynthesis, basic definition and raw materials require for photosynthesis .
Thanks for reading this post.
If you have any doubt or query or any suggestion please write to us. We will try to mention in our post.
I hope your online journey goes well.
You may also read this
Long distance transport in Plants.