Welcome to kashibiology.com
In this post we shall understand about about the definition, types, productivity and decomposition steps of ecosystem in detail for academic and medical competitive examination point of view.
Definition
Term ecosystem was coined by Tensley.
Ecosystem is the structural, functional, self regulated and self sustaining unit of our nature.
If we consider whole Biosphere as ecosystem, then it represents as a Global ecosystem.
Types of Ecosystem
Ecosystem can be classified into different categories on the basis of location, stability size and formation.
you may like to read ELISA & Its Protocol
On the basis of location
It includes
Terrestrial ecosystem
Such as Forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystem and desert ecosystem etc. which are exist on land.
Aquatic ecosystem
Such as pond ecosystem, Ocean ecosystem and other water bodies ecosystem, which are naturally found in the water bodies either freshwater or marine water.
1-On the basis of Stability
Permanent ecosystem
Such as forest ecosystem, Ocean ecosystem, grassland ecosystem. these are the naturally occurring ecosystem
Temporary ecosystem
Most of the temporary ecosystem is man made such as crop field or aquarium.
2-On the basis of Size
Micro ecosystem
Which are very small in size such as aquarium, crop field.
Macro ecosystem
Which are very large in size such as forest ecosystem, Ocean ecosystem.
3-On the basis of Formation
Natural Ecosystem
Which naturally exist on the earth.
For example- grassland ecosystem, pond ecosystem etc.
Artificial Ecosystem
These are the man made ecosystem.
For example crop-field, aquarium.
Stratification
It is defined as the vertical distribution of different species occupying the different levels in an ecosystem.
Actually it is represent the height wise arrangement of species in a particular ecosystem.
For example-
in the forest ecosystem trees occupies first or top level in vertical strata or layer.
secondly shrubs occupy the vertical strata or layer.
At the bottom or last level herbs or grasses which are the smallest plant size wise, occupy the strata or vertical layer.
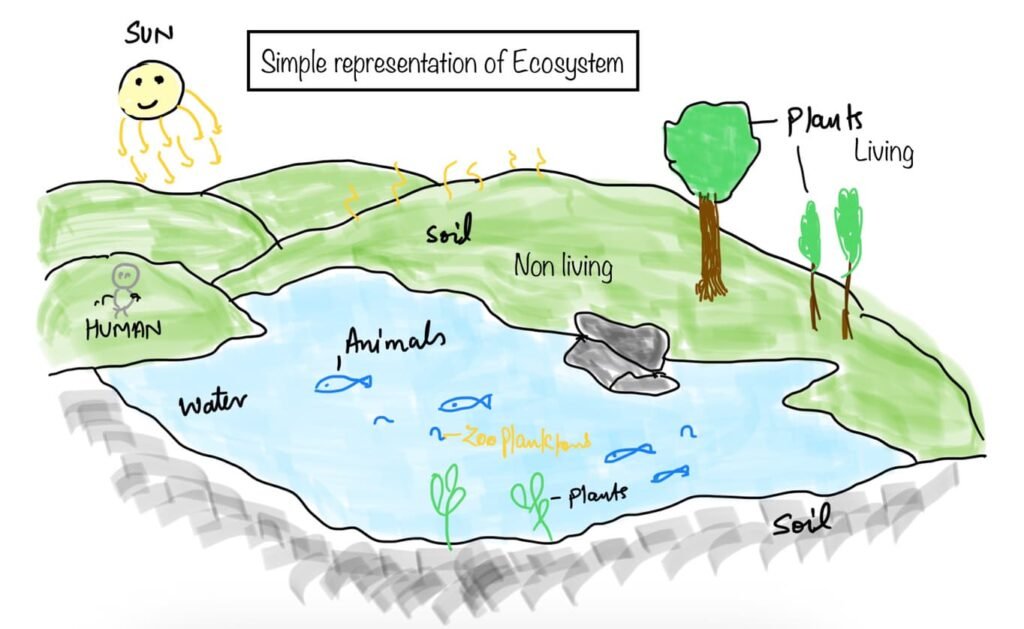
Components of Ecosystem
Ecosystem comprises of biotic components and abiotic components biotic components includes the living beings while the abiotic components includes non living things.
Biotic components
These include-
- Producers
- Consumers (primary, secondary and top consumers)
- Decomposers
Producers
These are autotrophic organism also called the transducers all the green plants and Organisms which are autotrophic in nature. they are responsible for the production of biomass by the photosynthetic process.
Consumers
They are heterotrophic non photosynthetic organism and further classified into primary consumer, secondary consumer and tertiary or top consumer.
Primary consumers
They are heterotrophic herbivorous animals and other organisms which are directly obtain their nutrition from the plants.
Secondary consumers
They are the Carnivorous animals which obtain their food material from the primary consumer.
Tertiary or top consumers
They include those animals which obtain their food from primary as well as secondary consumer directly.
In case of human and some other animals, they behave like omnivorous.
That is both carnivorous and omnivorous in nature, because they can obtain their food directly from plants or from consumers.
Decomposers
They are the mostly microorganisms such as Bacteria, fungi and other organisms.
They are also called reducers decomposers also includes detrivores and parasitic organisms.
Abiotic components
- Temperature
- Light
- Wind
- Soil
- Water
- Organic chemicals
- Inorganic chemicals
Function of Ecosystem
An Ecosystem is self sustain by the following processes namely-
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Energy flow
- Nutrient cycling
Let’s deal each of the topics separately to more understanding.
Productivity
The rate of biomass production is called productivity.
Primary productivity
Synthesis of biomass by photosynthesis at given time in a particular place.
It is representing as kilo calorie per meter square per year.
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
Total biomass production in an ecosystem by photosynthesis.
Net primary productivity (NPP)
Store weight of organic matter by producers after respiration.
GPP-R = NPP
NPP available biomass or organic matter for consumers.
Secondary productivity
Formation of organic matter or biomass by consumers using NPP biomass.
Annual NPP of biosphere is about 170 billion tons in term of dry weight of organic matter.
In which 115 billion tons come from terrestrial ecosystem and 55 billion tons from aquatic ecosystem.
Some examples of biomass production by different ecosystem.
- Desert scrub- (10 kg/thousand square & NPP 0.7 tones/hectare/year)
- Temperate grassland- (20 kg/thousand square & NPP 5 tones/hectare/year)
- Savannah- (40 kg/thousand square & NPP 9 tones/hectare/year)
- Temperate coniferous forest- (200 kg/thousand square & NPP 8 tones/hectare/year)
- Temperate deciduous forest- (300 kg/thousand square & NPP 12 tones/hectare/year)
- Tropical deciduous forest- (360 kg/thousand square & NPP 15 tones/hectare/year)
- Tropical rainforest- (400 kg/thousand square & NPP 20 tones/hectare/year)
Factors affecting on productivity
- Solar radiation
- Temperature
- Moisture
- Nutrient
- Photosynthetic efficiency – such as C3 plant has low productivity as compared to C4 plant.
Decomposition
It is define as the process of breakdown of complex organic material into simple and inorganic form by the different types of decomposer activities.
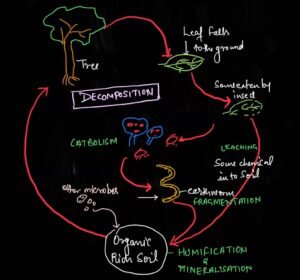
In natural ecosystem the process of decomposition involve following steps which are namely-
- Fragmentation
- Leaching
- Catabolism
- Humification
- Mineralization
Fragmentation
The process of fragmentation involved action of Detrivores on detritus.
Detrivores are the organisms such Earthworm and the insects which break down the large particles of plants and animal remains or waste into smaller particles.
Leaching
During fragmentation process some of the water inorganic minerals passes into the deeper layer of soil.
This process is called leaching. These minerals are normally not available for producers and precipitated as such.
Catabolism
The fragmented particles are further breakdown into inorganic chemicals in the presence of enzymes which are released by the microbes such as bacteria and fungi.
Here one important point is should be kept in the mind that the above three processes, that is fragmentation, leaching and catabolism not run one by other but operates simultaneously.
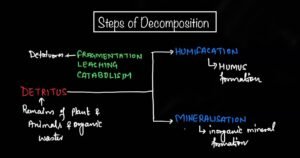
Humification
Humus is actually upper fertile part of soil.
Humification is the process in which humus is form. Humus is the dark colored amorphous (irregular in shape) substance.
It takes place during the mineralization and decomposition
Humus is resistant to action of microbes and decomposes in very slow manner. it has the variety of nutrients.
Mineralization
Humus further breakdown by some microbes and release a variety of inorganic nutrients in the ecosystem.
Factors affecting Decomposition
Aerobic condition
Oxygen require during decomposition. If oxygen is less or anaerobic condition is present the rate of decomposition is will be slow down.
Chemical composition of Detritus
If detritus has more lignin and chitin or more plant based waste, then it will be slow.
If detritus contain high nitrogen content and water soluble chemicals like sugar or glucose.
Climatic condition
In includes Soil moisture as well as temperature.
If the temperature is low& moisture is very less, then it will inhibit decomposition.
On the other hand warm & moist condition will support the process of decomposition.
Conclusion
Hope you will learn and understand about the definition, types, productivity and decomposition steps of ecosystem. In the nest post we shall discuss other topics of this chapter.
How do you like this blog, do give your opinion or any mistakes or updates in the comment box.
Thank you so much for giving your precious time