Welcome to kashibiology.com
In this post we shall understand about about the Energy flow, food chain, food web, ecological succession and biogeochemical cycle in detail for academic and medical competitive examination point of view.
Energy Flow
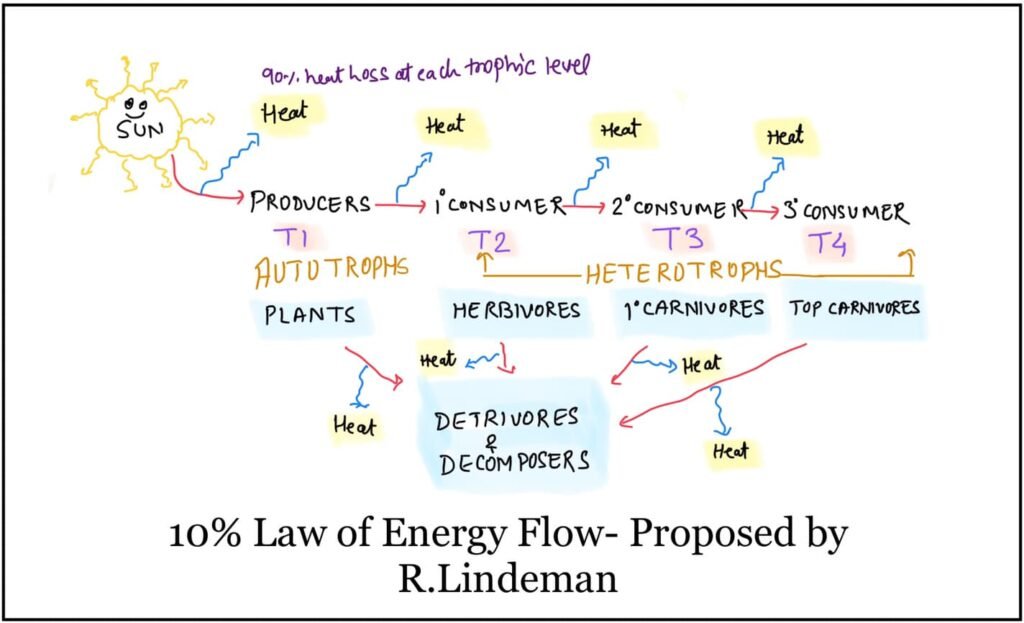
In the ecosystem the flow of energy in a unidirectional manner.
In all the type of ecosystem the ultimate source of energy is a Sun
However the total incident sunlight is not used by the living component of the ecosystem.
The producers or photoautotroph’s used 2-10% of incident energy of sunlight and used it in the process of photosynthesis.
Incident energy of sunlight is the ultimate source of energy to maintain the all the food chain or food cycle in the ecosystem.
Ecosystem class 12 NCERT notes part one
However during the transfer of energy from one trophic level to another trophic level 90% of energy loss in the form of heat and only 10% of energy pass to next topic level.
This concept of 10% of energy flow or transfer was given by Lindeman.
Food chain
It is the nutritional connection between organisms of different trophic level, in terms of feeding purpose.
Such as in an ecosystem producers eaten by primary consumers (herbivores), primary consumers eaten by secondary consumers (carnivores) and secondary consumers eaten by tertiary consumers or top carnivores.
However the food chain naturally does not exist in the ecosystem.
Types of food chain
In nature different kinds of food chain exist namely-
- Parasitic food chain (PFC)
- Detritus food chain (DFC)
- Grazing or predatory food chain (GFC)
Parasitic food chain
Start from the host organism and ends to parasites
Detritus Food chain
Detritus Food chain start with the detrivores and ends with top consumer
Grazing food chain
Grazing type of food chain also called parasitic food chain is most naturally occurring food chain.
Grazing type of food chain starts from the producers and terminates at the top consumers.
In aquatic ecosystems, the grazing type food chain is the major channel for energy flow.
In terrestrial ecosystems, much larger fraction of energy flow takes place by the detritus food chain compared to grazing type of food chain.
Food Web
It is the natural interconnection of food chains. It is more real than the food chain and naturally exists in the ecosystem.
Food web is not as straight as the food chain. It provides alternate food choices to consumers therefore consumers become Polyphagous.
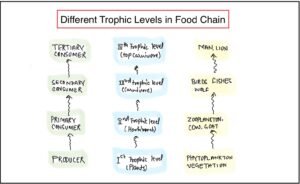
Trophic level
On the basis of the source of food in ecosystem organisms occupy a specific position in the food chain which is known as their trophic level.
Such as producers form the first trophic level, primary consumers form the secondary trophy level, secondary consumers form the third trophy level and the quaternary consumer or top consumer forms the fourth trophic level.
Ecological Pyramid
It was developed by Charles Elton in 1927. Hence it is also known as the Eltonian pyramid.
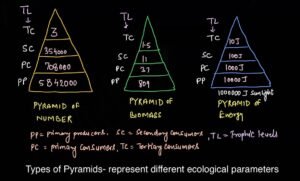
Ecological pyramid is the graphical representation of different ecological parameters, such as biomass, energy and number of individuals present in various trophic levels.
Types of Ecological pyramid
Pyramid of Number
As the type of food chain, It may be upright, inverted and spindle shaped.
Pyramid of Biomass
It may be erect or upright and inverted in shape as the food chain.
Pyramid of Energy
In every type of food chain the pyramid of energy is always upright or erected in shape, because in each trophic level during the flow of energy only 10% of energy is passed to the next topic level and 90% of energy is lost in the form of heat.
Limitation of Ecological Pyramid
However ecological pyramids provide rough estimation about different parameters of traffic levels but there are some disadvantages or limitations of ecological pyramids.
For example there is no place for saprophytes or decomposers in the ecological pyramid.
There is no organization that can arrange for the food web.
The ecological pyramid provides the idea of a simple food chain which never exists in nature.
In the ecological pyramid we cannot arrange some species which belong to two or more trophic levels.
Such as- Humans can take their nutrition from the plants as well as from the animals. In this case there is no fixed position of humans in the ecological pyramid.
Biotic or Ecological Succession
It is the natural development of a series of biotic communities at the same site one after the other and the process continues till a climax community develops.
The first community which develops during the ecological succession is known as Pioneer community.
The community which is stable and ultimately develops during ecological succession is known as the climax community.
In between the Pioneer community and climax community all the ecological succession communities are called transitional communities.
Changes during Ecological Succession
- Increase of biomass.
- Increase of soil differentiation.
- Increase of humus content of the soil.
- Increase of less biodiversity to high biodiversity or species diversity.
- Small short lived plants replaced by large long lived plants.
- r-selection changes to k-selection.
- Increase of niche specialization.
- Increase of stability
- A simple food chain becomes a Complex Food Chain and Food Web.
- Environmental stability increases.
- Productivity increases.
Types of Succession
There are two types of succession namely primary and secondary succession.
Primary succession
It is also called prisere.
In this process the area where no living organism ever existed such as-
Bare Rock area, newly cooled Lava or newly settled pond and there is no soil initially present.
The organism here slowly exists but the process is very slow and it will take a thousand or more years.
Secondary succession
It is also known as subsere.
In this condition, life was initially present but destroyed due to fire, flood or other natural disaster.
In this case there is some amount of soil or sediment present. Hence it is the fastest process than the primary succession.
It will be completed in 50-200 years for the grassland ecosystem.
For 100 to 200 years for the forest ecosystem.
Fugitive species
Species that are adapted to colonize newly disturbed habitats are called Fugitive species.
Standing state
It is defined as an amount of nutrients such as calcium phosphorus nitrogen carbon etc. present in the soil at a given time.
Nutrient Cycling or Biogeochemical cycle
(Bio=living, Geo=rock, air, water)
Types of nutrient cycle
Gaseous cycle such as carbon & nitrogen cycle
Sedimentary cycle such as phosphorus & sulphur cycle.
Carbon cycle
The cyclic circulation of carbon between the components of the ecosystem is called the carbon cycle.
In nature 71% of carbon is found dissolved in the ocean as a reservoir. Therefore oceanic reservoirs regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The atmosphere contains 1% of global carbon.
Fossil fuels the reservoir of carbon.
About 4 into 10 to power 13 kg carbon fixed by photosynthetic process per year.
Rainfall input of carbon is high.
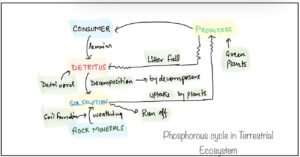
Phosphorus cycle
It is defined as the circulation of phosphorus between the living and nonliving components of an ecosystem.
The natural reservoir of phosphorus is the rock which contains Phosphorus as a phosphate.
Rainfall input of phosphorus is very less.
The gasses exchange of phosphorus between organisms and environment are also negligible.
Ecosystem services
The products and processes of the ecosystem are known as ecosystem services.
For example-
- Purification of Air by forest.
- Minimization of drought floods and other natural disaster
- Bio-geo-chemical cycle or nutrient cycling.
- Formation of fertile soil
- Maintenance of biodiversity or species diversity.
- Crop pollination.
- Provide storage site of carbon.
- Provide wildlife habitat.
- Provide social, cultural and spiritual values.
Apart from the above a lot of services provided by ecosystem which are impossible to mention here.
Ecosystem price tag
According to Robert Constanza the price of ecosystem services is 33 trillion dollars.
This value is just double the value of global gross national product or GNP.
In which 6% contribute habitat for wildlife formation
6% contribute climate regulation
20% recreation and nutrient cycling (10% for each).
50% and contribute soil formation.
Conclusion
Hope you will learn and understand about the Energy flow, food chain, food web, ecological succession and biogeochemical cycle, ecosystem services as well as some other important terms.
How do you like this blog, do give your opinion or any mistakes or updates in the comment box.
Thank you so much for giving your precious time