Welcome to kashibiology.com
In this post we have to learn about the ELISA in detail for academic and medical competitive examination point of view.
Enzyme immunoassays or Enzyme immunogenic test used an enzyme catalyzed reaction in detection of immunogenic reactions.
In the year 1971 Weeman & Schuurs& Engvall &Pearlmann described independently, how to use enzyme labeled agents in immunoassays.
ELISA or EIA
ELISAs are a type of immunoassays or immunogenic test that is commonly used to quantify labels of a specific target with in a sample.
you can also read Nucleotides & Nucleosides
Sample used in ELISA
The sample routinely used includes are-
- Serum (plasma – protein = serum)
- Plasma
- Cell culture supernatants
- Cell lysates
- Saliva
- Tissue lysates
- urine sample
ELISA are used and running in a 96 well microplates coated with the captured antibody specific for the analytes (sample of interest which to be detected).
Upon incubation with experimental sample standard or control, the target analytes is captured by this antibody or primary antibody.
A conjugated detection antibody or secondary antibody then binds to a different epitopes on the target analytes.
A substrate solution is added to produce a signal or colour that is proportional to the amount of analytes Bound.
Types of ELISA
Four main types of ELISA test namely-
- Direct ELISA
- Indirect ELISA
- Sandwich ELISA
- Competitive ELISA
Direct ELISA
In a direct ELISA an antigen or sample is immobilized directly on the plate and a conjugated detective antibody binds to the target proteins since only one antibody is used in a direct ELISA that are less specific other Elisa test
When to use?
While accessing antibody affinity and specificity investigating blocking or inhibiting interaction.
Advantage
Fast and simplest protocol disadvantage list specific because only one type of antibodies used
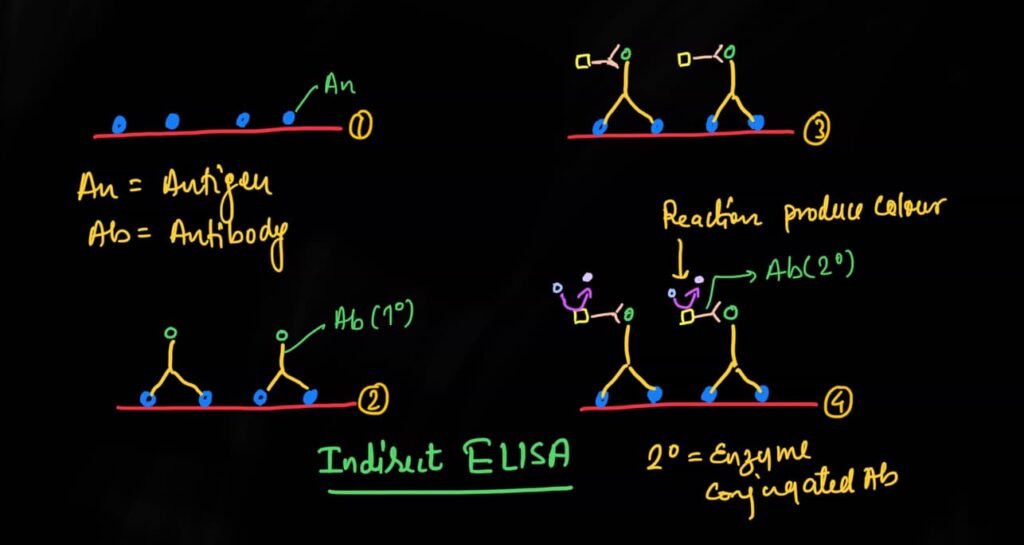
Indirect ELISA
Indirect ELISA is a similar to a direct ELISA in that it an antigen is immobilized on the plate, but it includes an additional step.
Firstan unconjugated primary antibody is added, that binds to the specific antigen.
Now an enzyme conjugated secondary antibody is directed against the primary antibody is added.
This is followed by addition of substrate which produces a colour product in a form of signal.
This signal is directly proportional to the amount of antigen bound in the well.
When to use?
For measuring endogenous antibody
Advantage
Amplification is possible using a secondary antibody
Disadvantage
Sometime secondary antibody can directly bind to antigen or potential cross reactivity exists because secondary antibody is being used.
Sandwich ELISA
This is most common type of ELISA.
Here two specific antibodies are used to sandwich the antigen.
Captured antibodies coated on a microplate.
Then sample is added and proteins of interest or analytes bind and is immobilized on the plate.
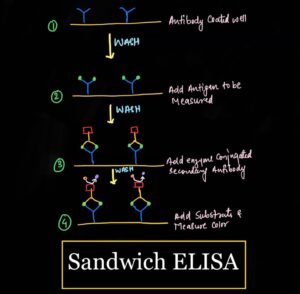
A conjugated detection antibody or secondary or antibody is in a date that binds to an additional epitopes on the target protein.
Substrate is added which coloured reaction product in the form of signal that is proportional to the amount of analytes or sample protein present in a sample.
Sandwich ELISAis highly specific since two antibodies is required to bind to the protein of interest.
When to use?
For determining the concentration of analytes in a biological sample.
Advantage
Highly specific and sensitive
Compatible with Complex sample
Disadvantage
Longer protocol that is time consuming
It has likelihood of errors.
Competitive ELISA
Competitive ELISA is commonly used in small molecules when the protein of interest or simple protein is too small to get efficiently sandwich between two antibodies.
Similar to sandwich ELISA a captured antibody or primary antibody is coated on a microplate, instead of using a conjugated antigen is used that competes for binding with the antigen present in the sample.
The more antigens present in sample the less conjugated antigen will bind to captured antibody.
Substrate is then added and colour reaction product generated.
The signal produced is inversely proportional to the amount of protein present in the sample.
When to use?
For determining the concentration of small molecules and hormones.
Advantage
Ability to quantify small molecule
Disadvantage
Less specific because only one antibodies used
Requires a conjugated antigen.
Components of ELISA
- Antibodies
- Matched Proteins
- Captured and Detection antibodies
- ELISA buffers
- ELISA plates
- ELISA plate reader
- Enzymes
- Substrate
- Protocols
The Components of Elisa and protocols are almost similar to every type of ELISA test but there is little variation.
Components of ELISA test
Antibodies
ELISA is highly dependent on the choice of antibody. Therefore any antibody that is used in detection or captured antibody should be checked for three criteria
1-Specificity
The antibody should bind to an epitope that is one specific antigen
2-Affinity
Binding should occurs rapidly and strongly
3-Avidity (Tight bonding)
Once bound, the antigen-antibody complex should be stable
Matched pairs
In a sandwich ELISA two antibodies are commonly referred as ‘Matched’ Usually matched antibody pairs are used in ELISA kit.
Captured and detection antibody
Both monoclonal and polyclonal antibody can be used in ELISA
ELISA buffer solution
A variety of buffer is needed including
- Lysis buffer
- Coating buffer
- Blocking buffer
- Washing buffer
- Dilution buffer
- Detection buffer
here we discuss not all but about some important buffers solution
Coating buffer
Requires stabilization of the antigen-antibody in order to promote passive adsorption to the microplate surface without changing the epitope.
Blocking buffer
They are added after the coating buffer, in order to prevent any non-specific binding of detection antibodies to the surface of the microplate .
Washing buffer
They are used between steps to remove any unbound material and need to be fully removed after their use. This buffer should be at the correct PH in order to stabilize their antigen-antibody Complex.
Detection buffers
They are composed of substrates needed for catalysis by the antigen-antibody Complex. Their composition must be strongly considered for accurate detection.
ELISA plate
Microplate or also called ELISA plate are available in a variety of formats including solid or strip well.
The most common plates are flat, well bottom and can have 96 or 384 Wells.
ELISA plate reader
The type of detection method used for ELISA will determine the type of microplate reader required for the signal output.
Types of reactions during ELISA assay
- Calorimetric reaction
- Chemiluminescence
- Fluorescence
Indirect ELISA
Protocol
Reagents and Equipment
- Phosphate buffer saline (PBS)
- Carbonate bicarbonate buffer (pH 9.6)
- Washing buffer (pH 7.4)
- Primary antibody (monoclonal in nature)
- Antibody controls
- Isotype matched, non specific antibody used as control for the primary antibody.
- Alkaline phosphatase enzyme (conjugated with secondary antibody)
- Substrate for alkaline phosphatase
- Stocking reagent for alkaline phosphatase
- Microtiter plates (usually 96-well)
- Microtiter plate reader (equipped with 405 nm or 450/492 nm filter).

Procedure
- Antigen coating
- Primary antibody reaction
- Application of secondary antibody
- Substrate preparation
- Development
Antigen coating
- Prepare an antigen solution at appropriate concentration in the carbonate bicarbonate buffer.
- Pipette 0.2 ml of the above solution to each well of the microtiter plate.
- Incubate at 47 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes or incubate overnight at 4 degree Celsius.
- Remove the coating solution and wash three times with PBS.
Primary antibody reaction
- Dilute the primary antibody in washing buffers.
- The optional dilution should be determinant.
- Add 0.2 ml of diluted monoclonal antibody or primary antibody to each well.
- Incubate at room temperature for 2 hours.
- Washed three times with PBS.
Application of secondary antibody
- Dilute the enzyme conjugated secondary antibody in PBS and add 0.2 ml of this solution to each well.
- Incubated at room temperature for 2 hour
- Washing three times with PBS.
Substrate preparation
During the last incubation, immediately before use prepare the enzyme substrate or bring premade liquid substrate to room temperature.
Development
- Add 0.2 ml of freshly prepared substrate to each well.
- Color should develop in well after 30 minutes (Which ranges yellow to orange in color)
- Absorbance may be read directly in a microplate reader at 405/450 nm.
- All the reaction may be stopped when 50 microlitre per well of the stopping reagent and absorbance is read at 405 or 492 nm.
Conclusion
ELISA is the important test used in different biological procedures such as disease diagnosis as well as forensic lab etc.
How do you like this blog, do give your opinion or any mistakes or updates in the comment box.
Thank you so much for giving your precious time

1 thought on “ELISA-Class notes Types, Protocol”
Good notes