Incomplete dominance and codominance 12th Biology
As we know that Mendel praposed three generalizations while hybridization experiments onpea plants. Which we know as Mendel’s Law of Inheritance or Principle of Inheritance. The names of these three laws are as follows.
first- Law of Dominance
second-Law of segregation or purity of gametes
third-Law of Independent Assortment
Among these three principles, due to many exceptions (which are naturally found in nature) to the Law of Dominance, it is no longer considered as a universal law.
Incomplete dominance and codominance also come as exceptions to this law(Law of Dominance). Out of which we will first understand incomplete dominance with an example.
Incomplete dominance
The condition or stage in which neither completely dominant nor completely recessive characters are seen in the F1 generation (first filial generation).
Rather, a new character is formed by mixing both, meaning that here the dominant character is not completely dominant but partially dominant.
After the discovery of incomplete dominance, similar experiments were repeated on other types of plants as well.
So it was found that sometimes the phenotypic character of the F1 generation does not match either of the two parent plants, or rather the character in between the two comes in the F1 generation.
Incomplete dominance was first discovered by Carl Correns. He observed and studied it on Mirabilis jalapa and Oenothera lamarckina plants.
And Carl Correns, on the basis of his experiments on this plant, found that not all plants follow the Law of Dominance in the same way.
And in some, incomplete dominance is found, there are many other examples of incomplete dominance. Like it is also found in Antirrhinum species plant.
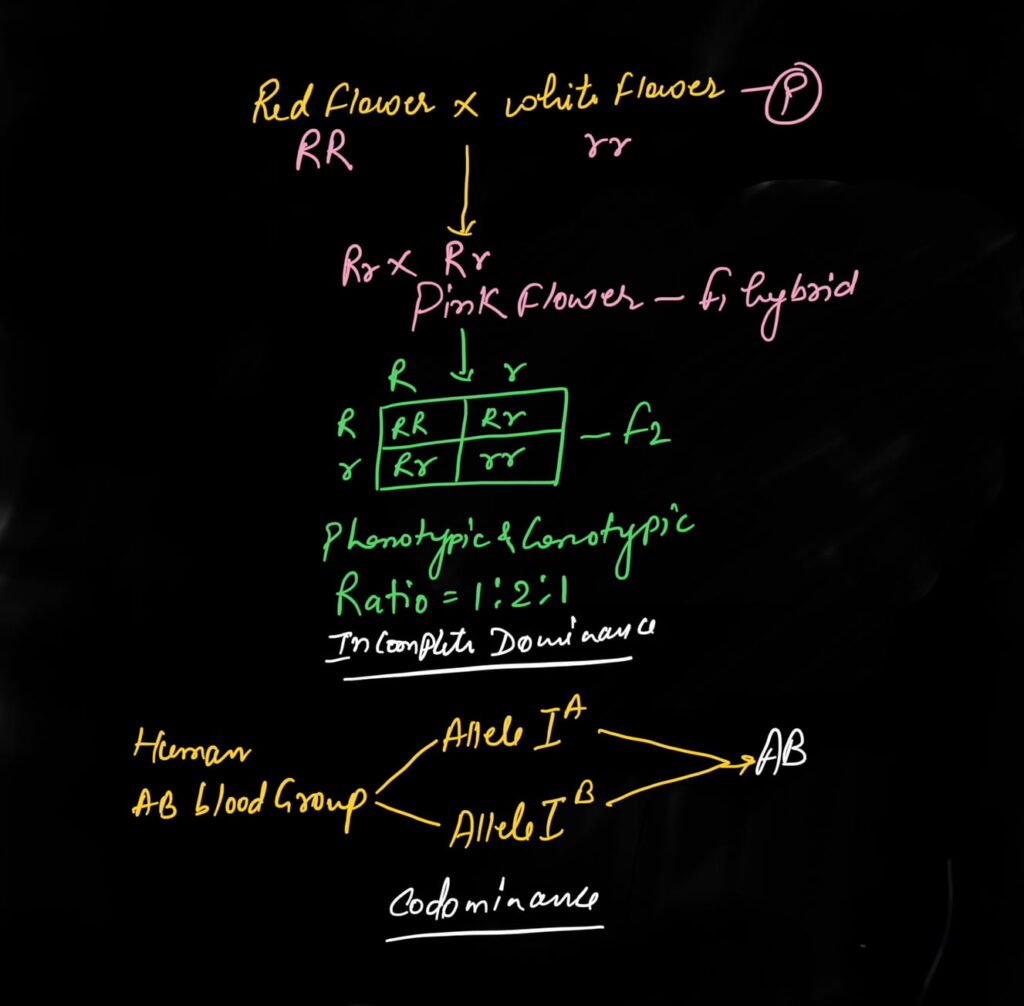
Inheritance of flower colors is a good example of incomplete dominance. Normally, red and white flowers are found in it.
When cross is done keeping in mind the characteristics of red and white flowers, then pink flowers are formed in the F1 generation.
But when F1 hybrids which have pink flowers are crossed, then in the F2 generation, there is a ratio of one red flower, two pink flowers, and one plant with white flowers.
Meaning, both genotype ratio and phenotype ratio are formed in the same way, in this way, the ratio of genotype is formed according to Mendel’s law.
But the phenotype ratio was different from Mendel’s first law. What is the reason for incomplete dominance? It can be due to mutation.
We know that any organism has genes to express its character.
Each gene is present in pairs, which are called alleles (alternative form of gene). One of these alleles comes from the mother.
While its other allele comes from the father. Both these alleles can be the same or different.
These alleles contain information that makes enzymes or proteins. Enzymes or proteins regulate the metabolic reactions of the cell.
The final form of which appears in the form of phenotype, which we know as character. If there is a modification in the allele of the gene of any organism, then there can be three possibilities.
The first abnormal enzyme will be formed, the second less effective enzyme will be formed, and the third enzyme will not be formed at all. Apart from the above mentioned possibility, in the second and third cases the phenotype will not be correct or a new type of trait will emerge.
Codominance
This is also an exception to Mendel’s law, in which both alleles represent their character in a similar way.
Meaning it is different from incomplete dominance in such a way that in incomplete dominance a new type of character was being formed due to both the alleles, meaning a mixed character was being formed.
But in codominance both the characters will appear separately in the same individual.
For example, if we see the classical example of codominance, then the best example we see is AB blood group of humans.
Apart from this, the skin or coat color of cattle will be visible, you will see the coat color in dogs and cats in the same way.
You must have often seen that in many cows, the whole body is black, and there are white spots here and there.
Similarly, in dogs, cats and horses, you must have seen that the body is of one color and there are white spots on it.
So this means that one of their mother and father can be black and the other can be white and both the colors will be visible in their skin.
In biological or genetics language, these are called Roan, which means if we speak in Hindi, the color of the spotted body.
Let us assume that here the skin of the mother (female parent) cow is black, and her father (male parent) is white, then the new generation of calves will have a black body and white spots or a white body and black spots.
I hope you have understood this.
In the same way, when we talk about AB blood group of humans, then here both the alleles code both the antigens (antigen A and antigen B). Due to which both the antigens are found on the surface of RBC.
This is why such people have blood group AB, not A and B blood group.
So in codominance the alleles of both the genes are equally codominant to each other.
So in this way, we tried to understand the questions given below in today’s post.
-differentiate between incomplete dominance and codominance?
-explain the law of dominance and compare how it differs from incomplete dominance and codominance?
-explain incomplete dominance and codominance?
Conclusion
In this post, we have tried to learn some important and basic points related to the two important topics of genetics, that is; codominance and incomplete dominance, and have also shared important questions.
But still, if you see any kind of suggestion or update and any mistake, then you must tell us.
We will try our best to update your suggestion or any mistake, which has happened somewhere in the post.
Thank you very much for giving your valuable time.
Hope You Have a good online journey.