Welcome to kashibiology. In our last post we discussed over all concept about the Osmosis under Plant biology so in this post we’re about to unfold the Concept & Theories of about Water Translocation in Plants.
Water Translocation in Plants
Plant body specially designed to absorb water from the soil and further transport to the upward direction that is towards the shoot tips.
According to Ditmer in a four months old Rye plant (botanical name- Secale cereale) root has length about 620 km with per day increase of 5 km.
The root hairs in the root are the most efficient structure for water absorption.
In each root zone thousand of root hair cells are present.
such as in 4 month old Rye plants about 14 billion root hairs with a length of over 10,000 km present.
The above forms a total surface area of about 400 square meters.
Root hair cells are especially designed for water absorption.
They are filled with Osmotically active cell solution and centralized vacuole is present.
The cell wall of the root hair cell is thin and permeable to water.
Mechanism of water transport in Plants
The transport of water in plants takes place into separate steps .
number one- is absorption of water from the soil to root hair and from root hair cells to root of xylem
number two- is ascent of sap or upward movement of water. It is the movement of water from the xylem to upward direction.
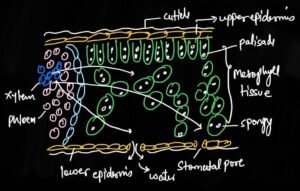
What is the absorption of water?
The absorption of water involving the local transport that is from soil to root hair cell and then to the xylem of root
The local movement of water take place by two separate pathway
One is the Apoplast pathway and the other is the Symplast pathway.
Both are the local means of water transport and the direction of the movement is from the soil to root hair cells and towards the Xylem tissue.
Apoplast pathway
This process involves the movement of water without the crossing of plasma membranes.
It means water moves through the cell wall or intercellular spaces.
Most of the water moves by this process because there is no disturbance for crossing of cells.
Hence it is a fast process and water easily moves from the root hair cell to the xylem.
Symplast pathway
Water move through the cell it means movement of water take place Cell to cell by plasmodesmata connection
The plasmodesmata are the small pore present between two adjacent cell
This is a time consuming process, therefore movement of water is slow.
Water moves passively as well as actively in the plant body.
Ascent of sap (upward movement of water)-
This is the upward movement of water.
A number of concepts have been proposed for the water moment from root to the upward direction.
The most accepted theory is the cohesion tension transpiration pull theory for the ascent of sap.
Actually sap is not only water but also the dissolved solutes molecule which is transported along with water.
Theories of Ascent of sap
Some common theories for ascent of sap and objection on theory are as follows-
Vital Theory-
It was proposed by J.C.bose Godlewski, Jansen, Strasburger.
According to vital theory the cortical cells directly pump water in the xylem after absorption of water from the external environment.
This theory is also known as pulsation theory
Objection
The objection to this theory is that the living cells are not involved in ascent of sap or an upward movement of water.
Root pressure theory-
It was proposed by Priestley, Stephen Hales and Stocking.
According to this theory pressure developed in root help in the movement of water in plants.
Objection
The main objection on root pressure theory are-
1-Root pressure is not present in all the types of plant.
2-It varies with the season like in spring and rainy season root pressure is high, while in summer it is less or even absent.
3-Root pressure is not sufficient to move water in tall trees (that is trees which are up to hundred meters or more tall).
4-Root pressure normally seen in the night.
Physical Theory (Cohesion-Tension Theory of Transpiration Pull-Dixon & Jolly)-
It was also known by other names, that is Capillary theory (Boehm), Imbibition theory (Unger & Sachs).
Cohesion tension theory also known as Dixon theory of ascent of sap, proposed by Dixon and Jolly in 1894 and it was further updated by Dixon in 1914.
Before starting the concept of cohesion tension theory, let familiar with some important terms-
Cohesion & Cohesive Force-
It is the mutual attraction between similar types of molecules such as attraction between water and water.
This mutual attraction between water molecules is due to the formation of of hydrogen bonding.
Adhesion & Adhesive Force-
It is between different chemical molecules such as in between water and lignin or water with polar molecules.
Lignified cell walls of tracheids and vessels of the xylem help in the attraction of water and its upward movement in the plant body.
Surface Tension-
According to this water molecules are attracted to each other in the liquid phase more than in the gaseous phase.
Transpiration-
Loss of water in the form of vapors from the aerial surface of plants, especially from the stomata, is known as the Transpiration.
How Ascent of Water occurs
The above characteristics (cohesion, adhesion, surface tension & transpiration) give the ability to plant pull water at the shoot tip from the root tip.
These create the following properties in plants namely-
Tensile strength and Capillarity
Tensile strength is the ability to resist a pulling force.
Whereas the Capillarity is the ability to rise of water in thin tubes.
The thin tubes work performed by the tracheids and vessels of the xylem.
Due to transpiration the water moves towards a Leaf because a thin film of water over the cell is continuously formed.
Therefore water molecules move towards the leaf from the xylem.
we know that concentration of water vapors is lower in atmosphere as compared to inside the leaf
Thus water easily diffuses into the surrounding environment and this creates a pull.
The speed of Upward movement of water molecules is about 15 meters per hour.
Conclusion-
Hope after reading this post you will be able to understand how the water is transported in up to 100 meters tall trees or even more.
Thanks for reading this post.
If you have any doubt or query or any suggestion please write to us. We will try to mention in our post.
I hope your online journey goes well.
You may also like to Read this….

