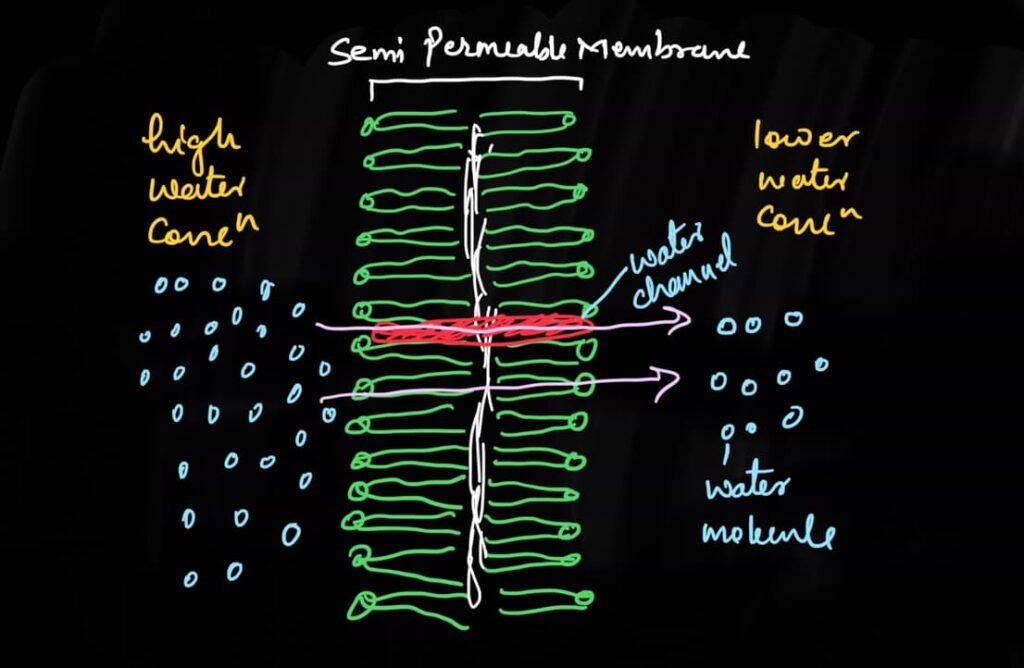
Osmosis- A process by which Living system absorb Water:
It is a special type of diffusion of water that occurs through a semipermeable membrane.
Term osmosis is mainly concerned with the local transport of water molecules between the cells and cell to its external environment through the semipermeable membrane.
There are many definitions of osmosis which defines the concept of Osmosis.
we will try to understand each and every definition in respect of osmosis.
- 1:The movement of solvent molecules from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration through the semipermeable membrane is known as osmosis.
- 2: The movement of water molecules from its higher concentration to its lower concentration through the semipermeable membrane is called osmosis.
- 3: The movement of water molecules from high water potential or chemical potential to less water potential or chemical potential area through the semipermeable membrane is called osmosis.
- 4: The movement of water molecules from high diffusion pressure area to lower diffusion pressure area through the semipermeable membrane is called osmosis.
Here in each definition the term semi permeable membrane is used and in each definition the concept of osmosis is defined.
Actually Osmosis is the local mode of transport of solvent, especially water molecules.
What is the Importance of Osmosis?
Osmosis play following significance role in living organisms-
- 1-Absorption of water by root.
- 2-Cell to cell movement of water.
- 3-Maintain turgidity of the cell.
- 4-Prevent collapsing of cell organelle.
- 5-Help in growth of radicle (future root) and plumule (future shoot) during seed germination.
- 6-Folding and dropping of leaves in the Mimosa pudica plant.
- 7-Opening and closing of stomata.
- 8-High osmotic pressure protects plants from drought and Frost injury.
Let’s understand the permeability of membranes.
This ability of plasma membrane to allow the passage of gases, liquid and solute molecules (dissolved substances) across it.
That is from the cytoplasm to the external environment of the cell or from the external environment to the interior of the cell.
On the basis of permeability, there are different types of membrane namely-
Impermeable membrane-
The membrane which does not allow anything to move across to it. For example suberised cell wall cutinized cell wall
Permeable membrane-
Such a type of membrane which allows the passage of all types of substances.
Such as a cell wall which consists of cellulose.
Semipermeable membrane-
The membrane allows movement of solvent molecules but not solute particles.
for example egg membrane, animal bladder and parchment membrane.
Selectively permeable membrane-
The membrane which is normally semi permeable but allows selective movement of solute.
for example plasma membrane or cell membrane and tonoplast which is the membrane of vacuole.
Types of Osmosis
On the basis of direction of movement of water molecules from cell to cell and the relative concentration of solution within the cell and outside the cell.
Osmosis is of two types-
Endo osmosis-
It is the movement of water molecules from the external environment to cell cytoplasm.
when a cell is placed in a highly diluted solution. It means the solution has higher concentration of water than the cell cytoplasm.
Then water molecules from the diluted solution will enter the cell cytoplasm resulting in the cell becoming swell.
Exo osmosis-
It is the moment of a water molecule from a cell to the external environment.
It is opposite to the Endo osmosis. That is when a cell is kept in a highly concentrated solution.
It means the solution has a high amount of solute molecules as compared to solvent molecules or water.
Then the water molecules come from the cell cytoplasm to the solution, resulting in the cell shrinking.
What is Water Potential?
In a pure water where no solutes molecules are present the water molecules are free to move randomly then the kinetic energy of water molecules is very high.
This is called the water potential. if any solute molecules added in a pure water then the water potential progressively decreases.
In standard condition the water potential is zero and it is measured in Bars or Pascal.
the greater the concentration of water, then the greater its kinetic energy and therefore greater the water potential in a solution.
Thus Pure water has the maximum water potential.
What is an Osmotically active Solution?
A solution which can cause an osmotic entry of water into it.
Such a solution is said to be a Osmotically active solution.
It possesses a low water potential.
Therefore any solution with high solute concentration is called an osmotic active solution for example sugar solution, salt solution etc.
What is Osmotic Pressure?
The pressure required to completely stop the entry of water into an Osmotically active solution across a membrane is called as Osmotic pressure.
Osmotic pressure of a solution is a measure of its tendency to take water by osmosis, the pressure applied by a solution to prevent inward movement of solvent or water molecules.
What is Reverse Osmosis?
It is the release of pure water from a solution through a semipermeable membrane.
reverse osmosis today is used in removing excess salt from the saline water as well as it is also used in extra purification of water in most of the water purifiers used in residential homes.
What is an Osmometer?
The instrument used to measure Osmotic pressure is called an Osmometer.
For example-
Berkeley and Hartley Osmometer.
Pfeiffer Osmometer.
Osmotic pressure is measures in atmospheric Bars or Pascal
1 bar is equal to 0.987 or 105 Pascal.
Conclusion
From the above description it is clear that osmosis plays an important role in the overall movement of water in the living system of either plants or animals or other organisms.
Therefore it is a very important process for the absorption of water and we know that without water there is no life.
All the metabolic reactions take place in aquatic medium as well as most of the solute molecules dissolve in water.
These dissolved solutes by the water circulation move from one part to the other part within the plant.
water it is essential to start the light reaction of photosynthesis in the leaves.
That’s why we often say “water is life”
Thanks for reading this post.
If you have any doubt or query or any suggestion please write to us. We will try to mention in our post
I hope your online journey goes well.
You may also like to Read this….
Short distance transport in plants.