Welcome to kashibiology.com
In this post we have to learn basic info about the Structure & Functions of Placenta for academic and medical competitive examination point of view.
Placenta
Placenta is a very close and internal connection, which is formed between the developing fetus and the womb of pregnant mother.
For the purpose of transport of nutrients, antibodies or immunogenic proteins, oxygen and other essential chemicals from the mother’s blood to the body of the fetus.
The excretory substances and carbon dioxide gas released from the fetus inside the exported to mother body.
Today’s post will focused on following questions that is-
What is the Placenta?
How Placenta Developed?
What is the Function of Placenta?
What are the Parts of Placenta?
When Placenta Formed?
On the seventh day after fertilization, the fertilized egg or blastocyst attaches itself to the walls of the uterus, this process is called implantation.
You may also enjoy reading this post- Excretory structures in Animals Groups
Shortly after implantation, the outer membrane of the blastocyst, called the trophoblast, divides into two layers.
The first layer is called the syncytiotrophoblast and the second layer is called the cytotrophoblast.
Chorionic membrane is formed from the trophoblast itself. Finger-like projections develop on the trophoblast on the outer surface of the chorion, which are called chorionic villi.
These chorionic villi begin to grow into the uterine tissue, and later play an important role in the formation of the placenta.
For this reason, the human placenta is also called chorionic placenta.
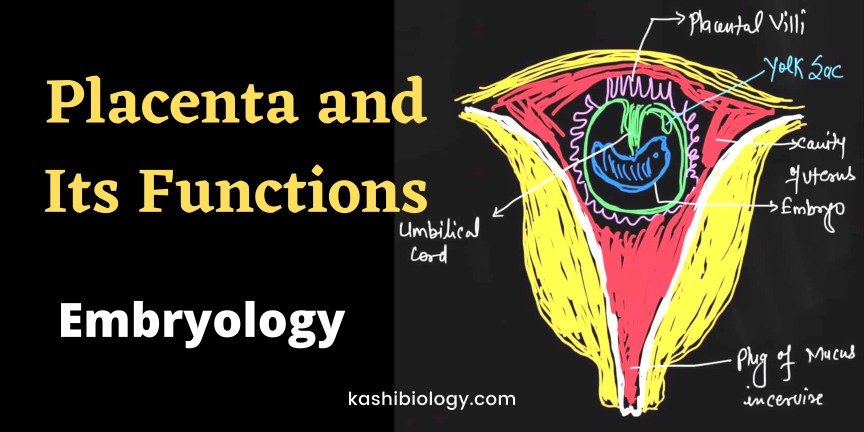
Parts of Placenta
The placenta consists of the embryonic part, chorionic part, and the mother’s decidua basalis.
Decidua basalis is that part of the endometrium of the uterus, which is formed between the chorion and the myometrium, so it is actually part of the mother’s uterus.
Wall of uterus has three tissue membranes namely- Endometrium, Myometrium and Perimetrium.
- The outer one is thin and called Perimetrium.
- The middle one is thick represents smooth layer called Myometrium.
- The inner most layers are glandular in nature called Endometrium. It is actually forms the lining of uterine cavity.
The attachment of the placenta to the mother’s uterus is so deep and intimate, that the blood vessels of the chorion are, in a way, directly connected to the mother’s blood.
The same placenta is attached to the developing fetus by the umbilical cord.
Function of Placenta
Performs many functions throughout the pregnancy which are as follows
1-Transport nutrients
All the nutrients that are present in the blood of the expectant mother and they are necessary for the development of the fetus, it is through the placenta that the fetus gets it.
2-Endocrine Function
The placenta also acts as a temporary endocrine gland.
It synthesizes and secretes different types of hormones through the pregnancy.
These hormones are necessary for the maintenance of pregnancy, and play an important role in the development of the fetus and also support the mother body in course of pregnancy.
Some of the main hormones released by the placenta are as follows-
3-Estrogen
Progesterone
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone
Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin (old name Human Placental Lactogen)
Chorionic corticotropin
Chorionic Thyrotropin
Relaxin
4-Storage organ
The placenta also stores food substances such as glycogen and fat, so that they can be used in time when there is a shortage of nutrients.
5-Prevention from Harmful Substances
The placenta also acts as an immune organ (not in true sense).
It allows the movement of only those substances which are necessary for the development of the embryo.
It blocks the entry of viruses, bacteria and many other medicines from the mother’s body into the fetal blood.
As well as, Placenta also allows antibody-G (Immunoglobulin-G) coming from the pregnant mother which is important for the natural passive immunity of the fetus.
For this reason this antibody-G is also called maternal antibody. However placenta itself not synthesized any antibodies.
6-In Respiration/Gaseous Exchange
The fetus requires oxygen in cellular respiration, which is supplied by the placenta from the maternal blood to fetus blood.
Simultaneously, the carbon dioxide that is releases in cellular respiration by the fetus is also diffused to the mother’s blood by the placenta.
7-In Excretion
All the excretory substances that are formed by the metabolic processes of the fetus, all of them are eliminated by the placenta in the mother’s blood.
Why advised to pregnant women to take healthy meals?
We all know that whatever we eat in the form of food is digested in gastro-intestinal tracts and then after absorption passed to blood circulation
And the digested food items from the blood are supplied throughout the body. Similarly during pregnancy, if the mother will take the more nutrient rich food (balanced diet in vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates and fats etc. are present in sufficient quantity).
It will go into her blood and after digestion and the fetus will get the necessary nutrients in the same way as it develops along with the mother’s body.
These nutrients are essential for the full development of the fetus, so during pregnancy, the mother should take special care of food for herself and her family.
Because as the mother will get food, the developing baby or fetus will also get the same type of food and it will develop accordingly.
Conclusion
Overall, we can say that the placenta acts as a bridge between the mother and the developing fetus or baby.
This connection is so intimate and strong, that is almost no virus, bacteria or harmful substances can enter the fetus or baby without the crossing of the placenta.
Therefore placenta is the actual barrier which decides what is enters the baby body and what is not.
This is a wonderful organ created by nature which is only developing in pregnant women and other placental animals.
The placenta does not perform any one of the functions instead of it works as multiple organs as much as require by the developing baby.
Placenta functions like a nutritive organ, excretory organ, respiratory organ, immune organ and endocrine gland etc.
This is the short discussion about the Placenta and its role. Hope you have to understand basic knowledge about this important structure which only develops during the pregnancy in all females’ placental mammals including human being.
If any suggestion or updating require from your side please comment us.
Thanks for reading the Post.