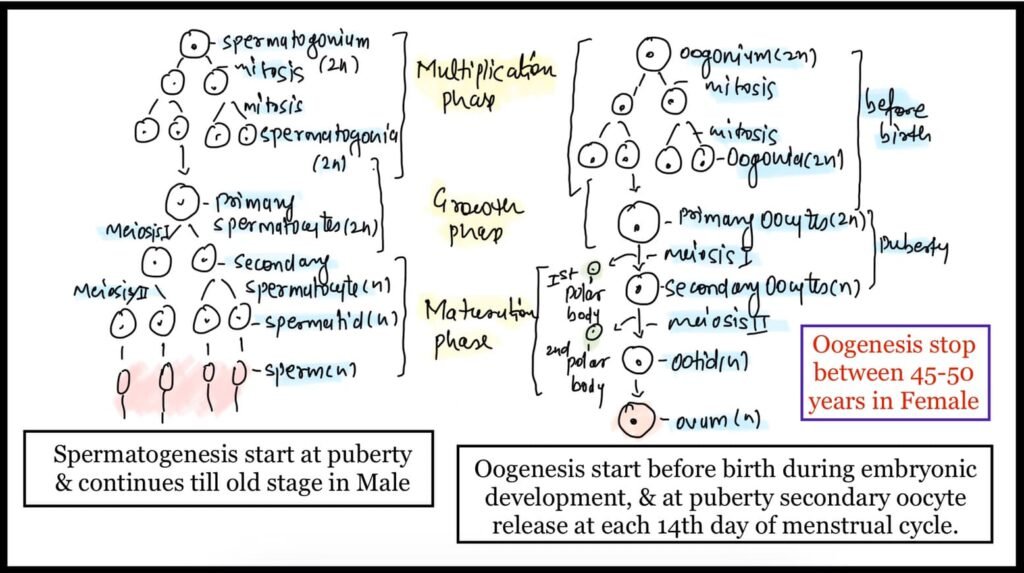
The process of formation of sperm or spermatozoa is called spermatogenesis; the process of spermatogenesis takes place in the primary reproductive organ that is, testis of male.
Similarly, the process of formation of ovum or egg is called oogenesis, and it takes place in the primary reproductive organ that is, ovary of the female.
for hindi click here
In female one ovum (in the form of secondary oocyte) is released in each menstrual cycle.
If fertilization of the ovum or egg occurs in the Ampullary-Isthmic junction of oviduct (fallopian tube), zygote formation take place, the zygote later develops into an embryo.
Our today’s post focused on the understanding the structure of male gamete that is Sperm or Spermatozoa.
Sperm-Male Gamete
Sperm or spermatozoa is male gamete which is microscopic and motile in size.
The total length of sperm is about 55 to 65 micrometers.
If sperm does not fertilize the ovum or egg within 24 to 48 hours after its release in the female genital tract, it is destroyed.
Hence their life span or life cycle is maximum 24-48 hours after release from the male body.
In the some research it is also claim that, the life span of sperm’s ability to fertilize an ovum is only about 6 hours.
Sperm is produced inside the male gonad or Testis by the process of spermatogenesis.
Sperm released from the seminiferous tubules of the testis by the process of spermiogenesis.
200-300 million sperms are released in a single ejaculation during coitus.
In which at least 60% of the sperm should be of the normal in size for fertilization, and 40% of the sperm should be very active and motile.
Structure of Sperm-Parts
There are 4 parts in the sperm, the first is the head region, the second is the neck, the third is the middle piece and the fourth is the tail part.
Head
It is the top most part, in which the Acrosome is present at the upper end.
Acrosome is actually the modification of Golgibody vesicles. Digestive enzymes are present inside the Acrosome.
These digestive enzymes digest the membrane of the ovum in the fertilization process. Due to which a sperm entry pathway is formed in the ovum and sperm complete the process of fertilization.
The following types of enzymes are present inside the Acrosome. All these are collectively called spermlysin.
For example-
- Hylauridonase
- Corona penetrating enzyme
- Zona digestive enzymes
A large nucleus is present just below the Acrosome.
Chromosomes (haploid DNA) are present inside the nucleus, which are haploid in number.
Neck
It is the very short region present just below the head region.
Neck contains proximal & distal centrioles.
The proximal centriole helps in first cleavage of the zygote after fertilization.
The distal centriole forms the axial filament. Axial filaments are made up of contractile proteins.
These axial filaments are extend from one end to the other in the tail part of the sperm.
The contraction of these proteins causes movement in the tail of the sperm, and the sperm moves in the fluid medium or seminal plasma.
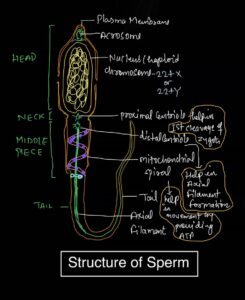
Middle piece
This part of the sperm is longer than the neck, and the mitochondria are present in the form of a mitochondrial spiral.
The number of mitochondrial spirals ranges from 10 to 14, which surround the axial filament.
Energy is released when the fructose present in the seminal plasma oxidized by mitochondria spiral.
This energy is given to the sperm in the form of ATP, and the sperm swim in the plasma medium.
Therefore the mitochondrial spiral is also known as the power house of sperm.
A ring centriole is present at the end of the middle piece, whose function is not yet well known.
Tail
Tail is the longest part of the sperm, has axial filament.
The total length of the tail is up to 50 micrometers.
As already mentioned above, axial filaments are made up of contractile proteins, which help in the movement of the tail.
In the transverse section (T.S) of the axial filament, it shows 9+2 arrangement (9+2 fibrils).
There are 9 peripheral fibers and 2 central fibers, similar types of arrangement visible in the internal structure of the centriole.
The axial filament is covered by a thin layer of cytoplasm.
Types of Sperm
Sperms can be of two types depending on the type of chromosome, 50% are sperms which have ‘X’ chromosome and 50% are such sperms which have ‘Y’ chromosome besides the autosomes.
Let us understand this with the help of an example, suppose if 300 million sperms are releasing in a single ejaculation.
So 150 million sperms will have ‘X’ chromosomes and the remaining 150 million sperms will have ‘Y’ chromosomes.
Now if the sperm with ‘X’ chromosome fertilizes with the ovum, then the zygote will develop into daughter or female.
On the other hand, if the ‘Y’ sperm fertilizes with the ovum, the zygote will develop into a son or male.
Hence it is completely depends on the chance, which sperm goes to fertilize with the ovum and the child will be male or female.
Therefore we cannot say to the female or the mother is responsible for a daughter birth daughter or son.
Rather it completely depends on the sperm of the man.
However, both the things are different in a way, because neither the father nor the mother can decide, whether the child to come will be a son or a son.
Ultimately it will determine by the nature. it completely depends on the chance which sperm fertilizes with the ovum and whether the offspring or progeny will be male or female.
Manchette Membrane
The posterior half of the nucleus, neck and middle piece are covered by a membrane called Manchette.
What is Semen?
As we know seminal plasma is released from male accessory gland (seminal vesicle, prostate gland and Cowper’s gland or bulbourethral gland).
When sperms come together in the seminal plasma, the liquid structure that is formed is called semen.
Semen is alkaline in nature, and this alkaline nature helps neutralize the acidity of the female genital tract.
Semen contains fructose sugar, prostaglandin hormones, clotting factors, calcium ions, mucus and various enzymes.
All are these help in fertilization, as well as help keep sperm alive.
Movement of sperm
Sperm moves in the seminal plasma at a speed of 1.5 to 3 millimeters per minute.
However, leukocytes of the female genital tract, especially leukocytes of the vaginal epithelium, destroy or engulf million sperm.
Conclusion
In today’s post, we understood about sperm and also learn that after fertilization there will be a son or daughter depends on the type of sperm which to be fertilized the ovum.
Hope you liked this post. Any kind of opinion or suggestion will be welcome from your side.
Apart from this, if there is any mistake, then also let us know, we will do our best to update it in the post.
Thank you for giving your valuable time.
Good luck on your online journey.