Transcription
The process of copying the genetic information present in DNA into RNA or in the form of RNA is called transcription.
or in simple language,
The process of making RNA from DNA is called transcription.
Gene expression requires the production of RNA, the process of transcription occurring in all organisms, whether prokaryotic cells or eukaryotic cells.
Even in viruses, the process of transcription is carried out in the host cell, whether it is an RNA virus or a DNA virus.
In today’s post we will try to understand the process of transcription.
What is Transcription?
In simple language, the process of making RNA from DNA is called transcription. Three types of RNA are needed to express a gene in any organism. A gene is the part of DNA that synthesizes RNA.
There are mainly three types of RNA, which are named-
- m-RNA- messenger RNA
- t-RNA- transfer RNA
- r-RNA- ribosomal RNA
These three types of RNA participate in the synthesis of proteins, and this protein further regulates the phenotypic features.
Proteins are involved in different metabolic processes, they can also be directly used as proteins, or they are converted into enzymes after modification, and participate in metabolic reactions.
All the metabolic processes take place in our body are enzymes catalyzed reactions.
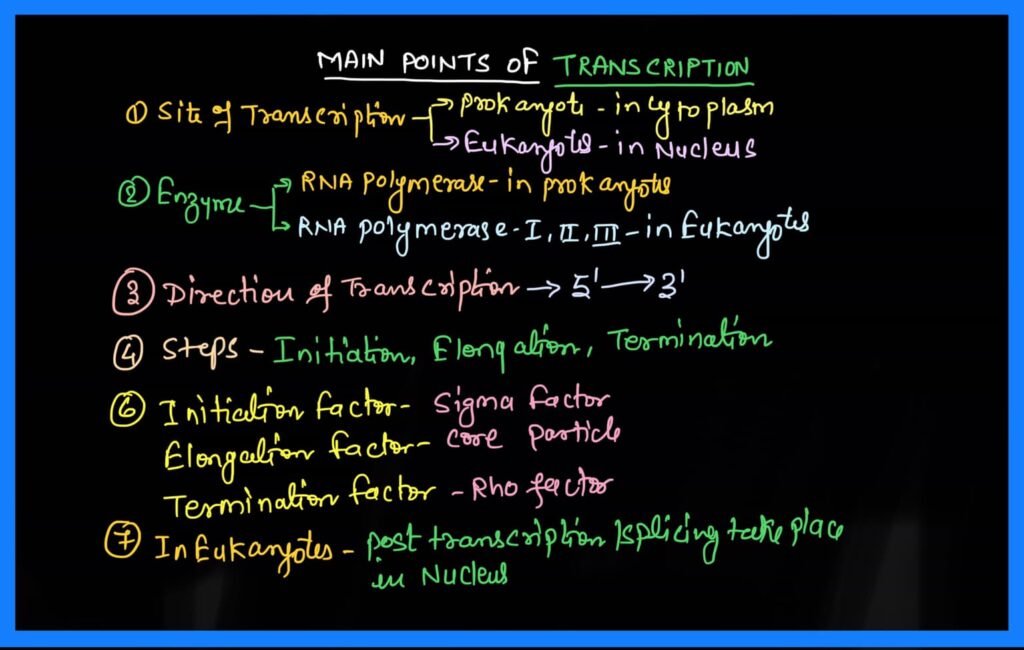
Site of Transcription in cell
The process of transcription in prokaryotes takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell because prokaryotes do not have a nuclear membrane, or a fully developed nucleus.
Simultaneously, translation starts along with transcription in prokaryotes.
In all eukaryotic cells, the entire transcription process takes place in the nucleus, because the well-developed nucleus is found in eukaryotic cells.
RNA polymerase Enzyme
The polymerase enzyme completes the process of transcription in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
This enzyme is a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme, which uses single-stranded DNA as a template, and performs transcription according to the complementary base pair rule.
By which RNA is formed from DNA.
In a prokaryotic cell, a single RNA polymerase enzyme synthesizes all three types of RNA.
RNA polymerase has two parts, the sigma factor and the core particle.
The sigma factor and the core particle when combined together to form a complete or holo RNA polymerase enzyme.
Sigma factor locates the promoter region in the DNA, and initiates transcription.
The same core particle elongates the RNA chain in the process of elongation.
Different genes may have different promoters, so different sigma factors have also been observed.
Such as-
The process of transcription in eukaryotic cells is a little more complex, so there are still different RNA polymerase enzymes here.
Which are written in Roman numbers, such as-
- RNA polymerase-I it transcribes r-RNA.
- RNA polymerase-II It transcribes hn-RNA or mRNA.
- RNA Polymerase-III It transcribes t-RNA;
in addition, RNA polymerase is also used for the transcription of other types of RNA.
Direction of transcription-
Transcription of RNA also takes place in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
Mechanism of Transcription
It is completed in three steps, and each step involves different enzymes and processes.
Initiation of RNA
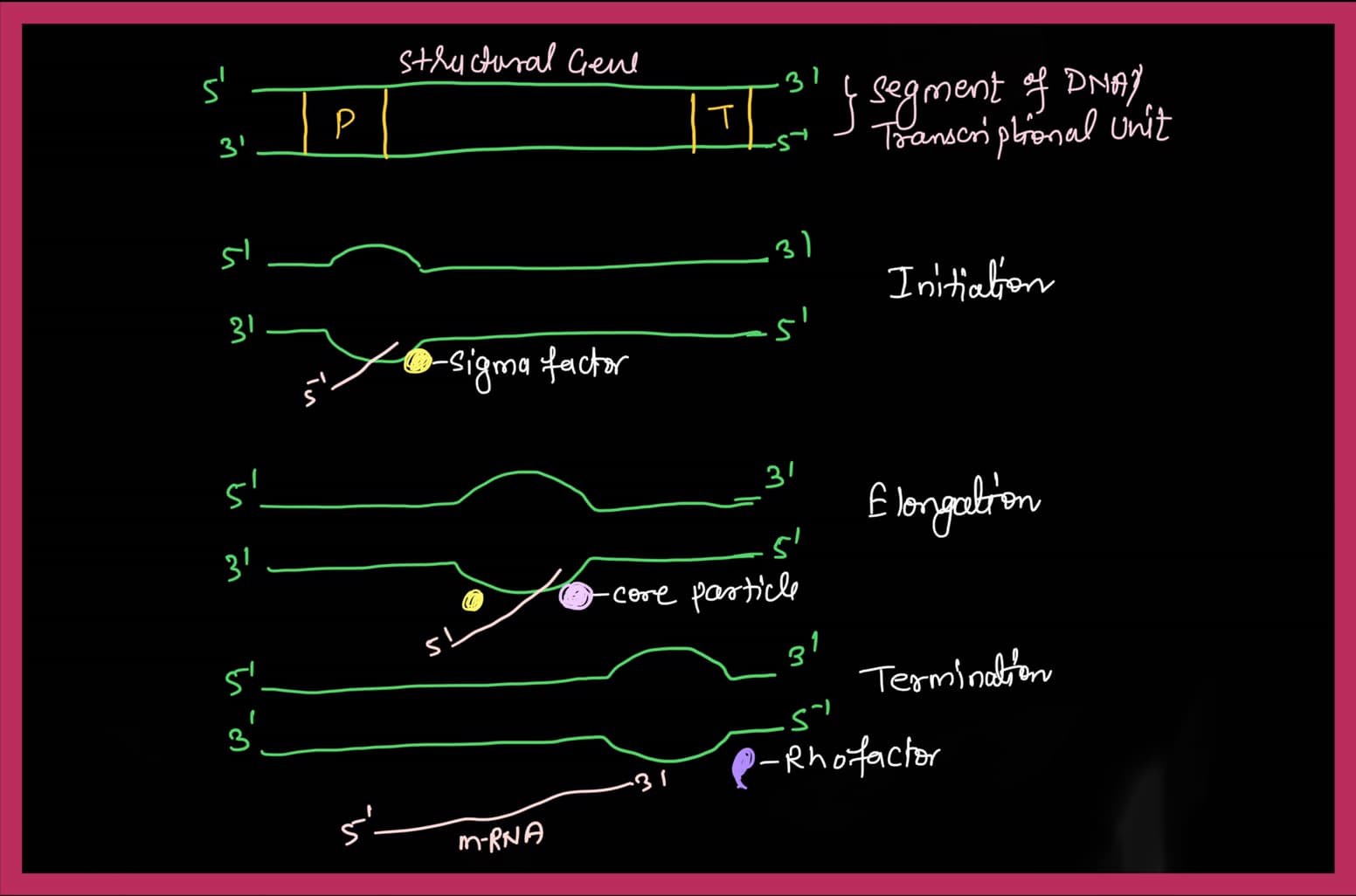
First, the sigma factor of the RNA polymerase searches for the promoter region in the DNA, and then binds to it.
This opens the promoter part of the DNA, and the initial transcription is completed.
RNA Chain Elongation
After the initial RNA formation or the process of transcription initiation, the core particle of the RNA polymerase comes and attaches to the DNA.
The core particle rapidly begins to add triphosphate to the new Note i in the 5′ prime to 3′ prime direction.
Due to which the growth of RNA starts faster in 5 prime to 3 prime directions.
However, when the nucleoside triphosphate is added, the core particle removes the sigma factor.
The core particle is also called the elongation factor and the core particle performs elongation at a speed of 35 to 40 nucleotides/sec.
When nucleoside triphosphate is introduced, two phosphates are released, and nucleoside monophosphate is added.
The two phosphates also act as energy sources.
RNA Termination
When the RNA chain or RNA is completely formed, the Rho factor, which is a protein, stops the process of transcription.
The Rho factor detaches the core particles of RNA polymerases from the DNA, thereby separating the RNA chain from the DNA.
In this way the process of transcription is also completed.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQ
What is a transcriptional unit?
The segment of DNA that is transcribed to form DNA is called a transcriptional unit.
Does transcription take place on both strands of DNA?
No, only the 3′ prime strand gets transcription.
What is the direction of RNA transcription?
The direction of RNA transcription is from 5′ prime to 3′ prime direction.
What is RNA Polymerase?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that participates in the formation of RNA from DNA
Why does both the strands of DNA not get translated?
If both strands of DNA are transcribed, the RNA will form double-stranded RNA by complementary base pairing.
Due to which the process of translation will not happen later. And even if both RNAs do translation, they will form different proteins. Due to which the metabolic process will not be done properly and different phenotypes will be seen.
What is the speed of RNA transcription?
The speed of transcription ranges from 35 to 40 nucleotides/sec.
Conclusion
If you have any suggestion or update of any kind and if you see any mistake then you must let us know.
We will do our best to update your suggestion or any mistake that happened anywhere in the post.
Many thanks to you for giving your valuable time.
Good luck with your online journey.