DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process in which an identical or carbon copy of DNA is made from one DNA to another. The mode of DNA replication is Semiconservative.
The mode of DNA replication is Semiconservative was first hypothesized by Watson and Crick, the same scientists who actually presented the famous Double Helical Model of DNA in 1953.
Also, read about DNA isolation kits
But DNA replication is Semiconservative, it was proved by two scientists named Mathew Meselson and Franklin Stahl while experimenting on E.coli bacteria in 1953.
you may also like to read this interesting post “A Love Story of RBC and Macrophages”
In today’s post, we will understand DNA replication in detail.
When cell division occurs in any organism DNA replication has already taken place.
Because whenever new daughter cells are formed from parental cells after division, it is necessary to distribute the right amount of DNA in them.
In eukaryotic cells, DNA replication occurs in the S-phase process of the cell cycle.
Whereas in case of prokaryotic cells, the process of DNA replication occurs just before cell division.
DNA replication occurs in the nucleus in eukaryotes, whereas in prokaryotes it occurs in the cytoplasm.
Because we know that the nucleus is not present in prokaryotes.
In the process of DNA replication, the two strands are separated from each other, and each strand begins to act as a template strand, and a new DNA strand is formed on these template strands.
That is to say, whatever daughter DNA molecules are formed, one of them is the old strand, and the other is the new strand.
That is why the mode of DNA replication is called the Semiconservative mode of DNA replication.
Enzymes of DNA Replication
More than 20 types of enzymes and proteins are used in DNA replication. In addition, ATP, magnesium ions, and deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTPs- dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and dTTP) are used.
dNTPs act dual functions they are a source of deoxynucleoside as well as the source of energy.
Some of the main enzymes that are used in DNA replication, their names and functions are as follows.
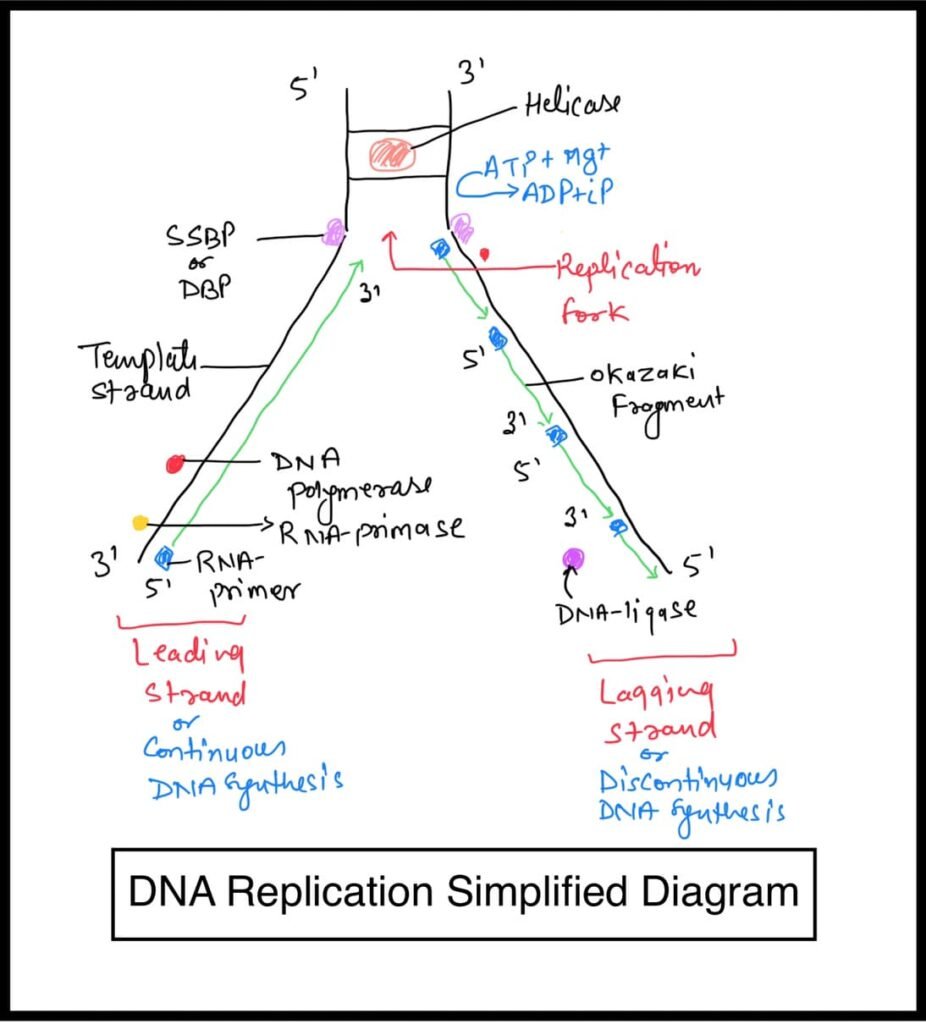
Helicase Enzyme
Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two complementary base pairs to separate the strand.
It is important to note here that the entire strand of DNA is not separated together during DNA replication.
Rather, the entire strand is opened in small segments at different positions, and the same process is repeated. This is mainly because opening a whole strand would require a lot of energy to completely separate the two strands.
Because it costs one ATP to break each hydrogen bond, you can get an idea of how much ATP would be spent in the separation of the complete strand completely. If the total length of human DNA is 6.6×109 base pairs, then how much ATP can be spent in total?
On the other hand, if both the strands are completely separated together, then both the strands will be separated from each other and scattered around in the nucleus. As a result, the replication will not happen properly.
SSBP/DBP
SSBP (Single Stranded Binding Protein) or DBP (DNA binding protein) holds both the separated strands like a clamp so that they cannot be rejoined. Because the renaturation power in DNA is very high.
If the separated strands are rewind, the helicase enzyme will again have to break the hydrogen bond and the cell will have to spend ATP again.
Due to this both time and energy will be wasted and DNA replication will not be completed at the right time.
DNA Polymerase
It helps in the polymerization of DNA, and it is the main enzyme for the synthesis of DNA.
DNA polymerases polymerize DNA in the 5′-3′ direction.
RNA Primase
It is a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme that aids in the synthesis of RNA, a short RNA formed at the 3′ prime end of the separated DNA template segment, prior to the synthesis of DNA.
This small RNA molecule is called RNA primer. The enzyme that makes it is called RNA Primase.
DNA Ligase
This enzyme works to join OKAZAKI (small DNA segments), hence it is also called a joining or sealing enzyme.
Rate of DNA Replication
The DNA replication rate is 2000 base pairs/second in the ideal condition.
This means that the DNA polymerase enzyme added 2000 bases every second on the template strand during DNA synthesis.
Origin of Replication (Ori)
It is the site in the DNA molecule from where DNA replication will begin.
Main steps of DNA replication
The main steps of DNA replication are as follows.
Unwinding of DNA Strand
Firstly, the helicase enzymes break the hydrogen bond, which causes the complementary base pair of the two strands to separate from each other and separate both the strand.
DNA replication begins at a specific point called the origin of application.
The two separated strands want to rejoin, which is prevented by a single-stranded binding protein or a DNA binding protein.
Primer Synthesis
The RNA primase enzyme synthesizes the small RNA molecule at the three prime ends of the template strand. Which is called RNA primer, this primer provides a free 3′ prime OH group.
So that the synthesis of DNA can be initiated by the enzyme DNA polymerase because DNA polymerase alone cannot initiate the synthesis of DNA.
DNA Synthesis/Chain Elongation
After the formation of the primer, the DNA polymerase starts the synthesis of DNA in the 5’ prime to 3’ prime directions.
Continuous DNA synthesis occurs on one strand of DNA. Whereas on the other strand, the synthesis of DNA takes place in segments.
These segments, called Okazaki segments, were first seen by Okazaki.
In prokaryotic cells, the Okazaki segment is 100 to 200 bases in length, while in eukaryotic cells it is 1000 to 2000 nucleotides in length.
Continuous synthesis occurs on one strand of DNA, this strand is called the leading strand, while the strand on which the DNA segment is formed is called the lagging strand.
Primer Removal
After the DNA is synthesized, the DNA polymerase enzyme removes the primer and adds new nucleotides at the gap.
Joining of Okazaki Segment
The DNA ligase enzyme cleaves the two Okazaki segments, a process that occurs after the formation of a phosphodiester bond.
Conclusion
Thus we have seen how DNA replication occurs in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and what their main enzymes are.
Although DNA replication is explained very briefly here, we hope you like it.
Any kind of suggestion or update and if you see any mistake then you must let us know.
We will do our best to update your suggestion or any mistake that happened anywhere in the post.
Many thanks to you for giving your valuable time.
Good luck with your online journey.