Health can be defined as a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not only absence of disease. If it gets disturbed by some outer agents it is called disease . Well this is not a perfect explanation for what disease is so let’s know this below .
What is a Disease?
Any alteration in the body for malfunctioning of the organ which affects the normal physiology of the body is called disease.
Definition of Symptom:
When the function of one or more organ or system of the body is adversely affected appear by various sign called symptom
What is Pathogen?
Those microorganisms which cause disease are called pathogens.
Most of the parasites are pathogen because they harm the host by living in or as that is Endoparasites or Ectoparasites on the body of Host
Some common pathogens are viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoans and helminthes.
Pathogens multiply and interfere with the normal vital activities of host resulting change in morphology and functional activity of the body
Examples of Some common diseases and their causative agents:
Bacterial Disease like Typhoid fever, Pneumonia
Viral diseases like Common Cold, AIDS and Polio
Protozoan diseases like Malaria, Amoebiasis
Helminthic diseases like Ascariasis, Filariasis
Fungal diseases like Ringworm
What is Incubation period?
The duration between the entry of pathogen into the host body and the appearance of first symptom of the disease is called incubation period
It may vary the type of pathogen and host
Types of diseases:
There are two classification of disease that is Congenital diseases and Acquired diseases.
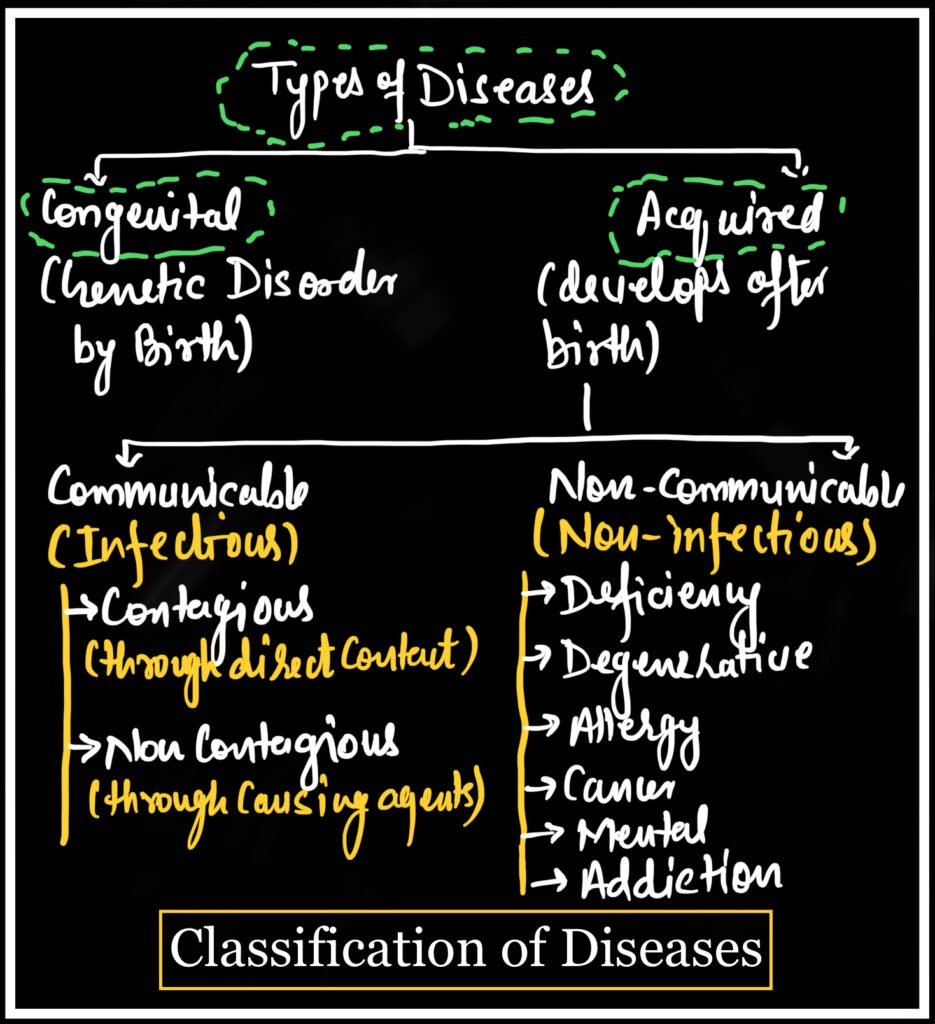
(A)Congenital disease:
It is present from birth and arises due to gene or chromosomal changes like Haemophilia, Turner syndrome etc.
(B)Acquired diseases
Disease developed after the birth and it may be communicable and non-communicable
(1)Communicable or Infectious diseases
Diseases which caused by pathogens like viruses bacteria. It may be Contagious or Non-contagious
(i)Contagious diseases
Diseases causing agent transmitted through direct contact for example ringworm
(ii)Non-contagious diseases
Disease causing agent transmitted through a vector example typhoid malaria dengue etc.
(2)Non-communicable or Noninfectious
diseases do not spread to other person by contact or any vector
(i)Deficiency diseases
It is due to the deficiency of nutrients hormones
examples diabetes, scurvy
(ii)Degenerative diseases
It is due to functioning of some important organs example heart disease
(iii)Cancer
It is due to uncontrolled growth of certain tissues and cells
(iv)Mental disorder
Such as depression, mental disability
(v)Addiction
It is due to drug or alcohol abuse
(vi)Allergy
It is due to the hypersensitivity of the body immune system against certain foreign substances called allergens.
Some common Pathogenic diseases–
Some common bacterial diseases–
1-Typhoid fever
This caused by bacteria Salmonella typhi
The pathogen present in the stool or maybe in urine. hence carried by water and contaminated food in a healthy person the
Incubation period is 1 to 3 weeks
Symptoms:
There is high fever and low pulse rate patient feel abdominal pain and passes frequent stool treatment the patient is treated with antibiotics such as Terramycin, Chloromycetin
Typhoid Mary:
It is a classical case in medicine Mary Mallon was a cook a typhoid fever carrier
She continuously spread typhoid fever for several years through the food she prepared.
2-Pneumonia:
It caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae
It is a serious disease of the lungs due to the infection of the alveoli or air sacs of lungs filled with fluid, which causes severe problems in respiration or breathing.
Symptoms:
Fever, chill, cough and headache
In severe cases lips and fingernails turn to bluish-grey colour
Transmission:
The transmission of bacteria take place by inhalation of the droplets or aerosols released by patient or even by sharing glasses utensils of infected person
Incubation period is one to three days
Treatment:
Use of Antibiotics such as Penicillin, Streptomycin and Ampicillin
Some common Viral diseases–
1-Common Cold:
It is caused by rhinoviruses that infect the nose and respiratory passage.
It is characterized by nasal congestion and discharge, cough, headache etc.
The symptoms usually last for 3 to 7 days.
Transmission:
It takes place by droplets of cough or sneezes of suffering person also transmitted through contaminated objects like pen book cup keyboard
2-Polio:
It is caused by poliomyelitis virus
This virus enters the body via the alimentary canal where it replicates and reaches to the nervous system.
Incubation period is 7 to 14 days
It cause inflammation of nervous system resulting paralysis of particular skeletal muscle
Treatment:
It is treated by oral polio vaccine (OPV) or injectable polio vaccine (IPV) developed by Salk and Sabin
Some common Fungal diseases
The study of fungal diseases in humans is known as Medicinal Mycology.
The most common fungal disease is-
1-Ringworm
It is caused by fungi belonging to genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton.
Trichophyton infect skin hair and nail
Epidermophyton infect skin and nail
Microsporum infect hair and skin
Symptom
The symptom includes dryness and scaly lesion
The lesson cause intense itching
Heat and moisture help to fungal growth
Transmission:
Ringworm are generally transmitted from soil or by using towels, cloth or even comb of infected individuals
Antifungal drugs are used to cure the disease
Some common Helminthic diseases-
It is caused by flatworms or and roundworms some common Helminthic diseases are given below
1-Ascariasis
It is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, which belong to nematodes.
It is an intestinal parasite and causes Ascariasis disease.
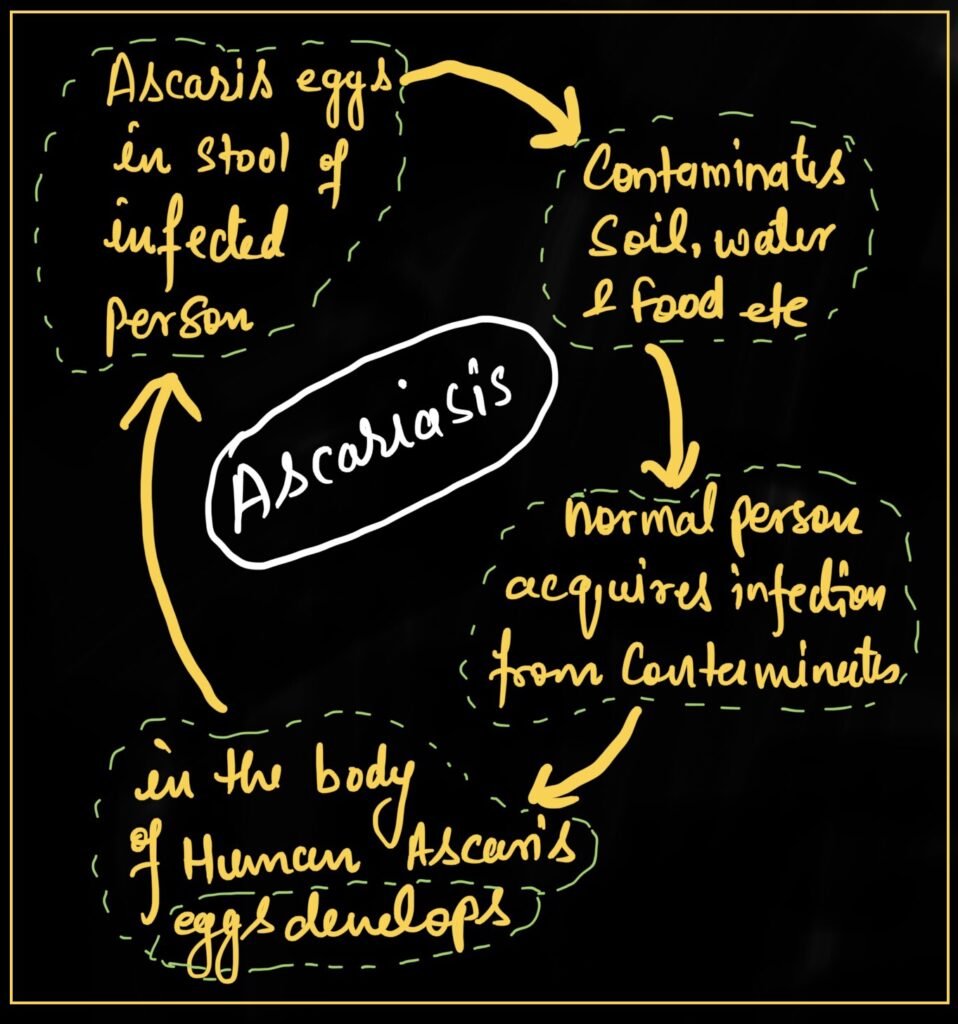
Symptom:
The diagnostic symptom include internal bleeding, muscular pain, fever, anaemia and blockage of the intestinal tract
Transmission:
The transmission takes place by contaminated soil water and food which carry its egg.
Treatment:
It is treated by band and Antihelminthic medicines
2-Elephantiasis/Filariasis disease–
Filaria is caused by filarial worm (Wuchereria bancrofti and Wuchereria malayi)

In Filariasis there is slowly developing excessive inflammation of the organs in which Filarial worms live for many years.
They usually occur in lymphatic vessels of lower limbs.
Sometimes the genital organs are also infected.
Transmission:
Filarial worm transmitted to a healthy person through the bite of a female culex mosquito.
Treatment:
Treatment involved use of medicines like Albendazole with DEC (Diethylcarbamazine)
Some common Protozoan disease–
1-Amoebiasis or Amoebic dysentery
It is caused by protozoan Entamoeba histolytica which is the parasite in the large intestine of humans.
The incubation period is about to 2 to 4 weeks
Transmission:
Mode of transmission involve the contaminated water and food
House flies act as mechanical carriers and help to transmit parasites from the stool of an infected person to a healthy person.
Symptoms:
The symptoms include abdominal pain, stool with excess mucus and blood clots, because it breaks RBC.
Prevention and Treatment:
The prevention involved avoidance of contaminated food and water and it is treated by metronidazole drugs
2-Malarial Fever-
Malarial fever is caused by protozoan parasite plasmodium there are different species of plasmodium such as
P. vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale, and P. falciparum which cause different types of malaria fever.
Off which P. falciparum cause more serious malarial fever which can be fatal
Life Cycle of Malarial Parasite-
The life cycle of plasmodium in wall to host that is female mosquito Anopheles and human female end of lease mosquito feed on you will be loved only can service vector when infected female Anopheles mosquito b a person the infection
The infectious form of plasmodium that is porous white enters the human body it multiplies within the liver cell and attacks the RBC.
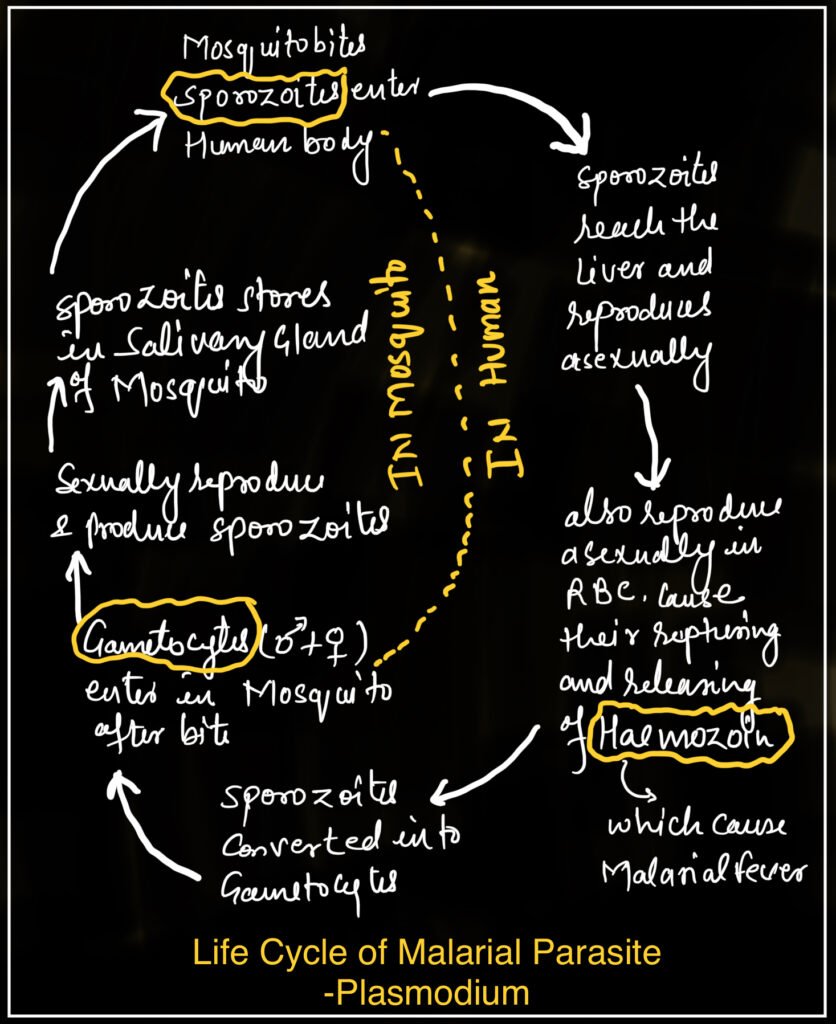
Resulting release of toxic substance after breaking off hemoglobin called Haemozoin.
Haemozoin is responsible for the chill and high fever and fever recurring every 3 to 4 days.
When Anopheles bite in person the infected stage Gametocytes(small male & large female gametocytes) enters the mosquito along with the blood meal.
In the stomach of mosquitoes, fertilization takes place and zygotes develop into Sporozoites.
The parasites multiply to form Sporozoites that are stored in the salivary gland of mosquito.
Symptoms:
The patient display loss of appetite, muscular pain, headache and chilling of the body
The temperature is starting to rise and may reach 106 degrees Fahrenheit. Patients show excessive sweating.
Incubation period:
For Plasmodium vivax is for 3 days
For Plasmodium falciparum 12 days
For Plasmodium malariae 28 days
For Plasmodium ovale for 3 days
Prevention:
Avoiding of stagnant water in around residential areas
Regular cleaning of household coolers
Use of mosquito nets and repellents, introducing Fishes like Gambusia in ponds that feed on mosquito larvae.
Spraying of insecticides in drainage areas and swampy area
Treatment:
Quinine is the oldest drug for malarial fever treatment which is obtained from the bark of Cinchona tree.
Other antimalarial drugs are Primaquin, Chloroquinine and Camoquin etc.
Species of plasmodium and types of malaria:
P.vivax cause benign tertian malaria in which fever reoccur after 48 hours.
P.falciparum cause malignant tertian malaria in which fever reoccur after 48 hours.
P.malariae cause quartan malaria in which fever reoccur after 72 hours.
P.ovale cause mild tertian malaria in which fever reoccur after 72 hours.
For part two notes click here

