Operon Concept
The operon was conceptualized (elucidated) by Jacob and Monad, while they were working on E.coli Bacteria.
An operon is a cluster of genes, where the product of one gene interacts with another gene. Such types of molecular interactions ultimately regulate one or more metabolic pathways by which phenotypic expression will express in any organisms.
You may also read this DNA Replication
Because any gene forms RNA or a protein, and the protein ultimately controls the phenotypic character in the organisms.
The most common and studied operon is the lac operon.
Lac (lac= lactose sugar) operon is related to the metabolism of lactose sugar.
An operon consists of a promoter gene, a regulator gene, an operator gene, and a structural gene.
The product of the regulator gene turns the operator gene off or on, depending on the structural gene to make m-RNA.
And if m-RNA is made, then it further translates. This protein or enzyme, from which the protein is formed, then regulates the phenotypic expression.
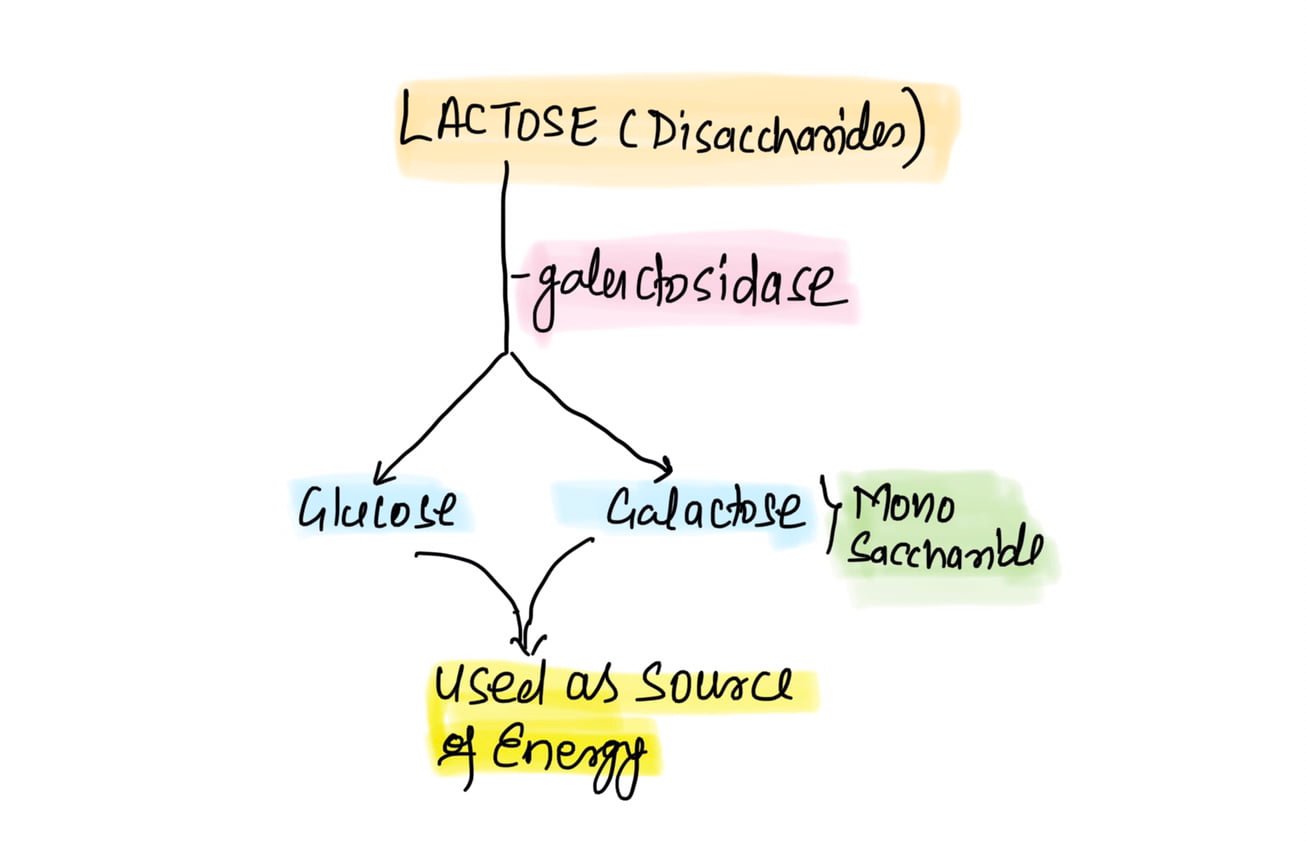
The metabolism of lactose sugar (lactose- a type of disaccharide) occurs in lac operon.
When the E.coli bacteria require energy, it breaks down the lactose sugar into glucose and galactose (glucose & galactose- types of monosaccharide) in the presence of the beta-galactosidase enzyme.
In this way, glucose and galactose reduce the energy source for E.coli bacteria.
But if there is no lactose sugar in the E.coli cell or in its surrounding environment, then the formation of beta galactosidase enzyme does not take place.
So far, operons of different types have been discovered, such as val-operon, trip-operon, his-operon and lac-operon (val-operon, his-operon, trp-operon & lac-operon etc.)
In today’s post we will learn about Lac Operon in detail, how it works.
Lac Operon
It was discovered and named by Jacob and Monad in E. coli bacteria, where lac refers to lactose sugar.
In this operon, lactose sugar itself acts as an inducer.
If lactose sugar is present in the E.coli bacteria, or in its external environment, then the beta-galactosidase enzyme will be formed, which will break down lactose into glucose and galactose.
Then the E.coli bacteria will use this glucose and galactose as an energy source.
But if E.coli bacteria do not have lactose sugar or lactose sugar in its surrounding environment, the formation of beta galactosidase enzyme will not take place.
Structural Gene of Operon
In lac operon, structural genes differentiate into three parts, their names are as follows.
Lac-z gene
The lac-z gene codes for the beta-galactosidase enzyme, which breaks down the lactose sugar into Glucose and Galactose.
Lac-y gene
The lac-Y gene codes for the permease enzyme that regulates the movement of lactose in E.coli.
Lac-a Gene
The lac-a gene codes for the trans-acetylase enzyme, which regulates the concentration of toxic chemicals produced during metabolic processes in the cell.
Mechanism of Operon
We divide the Lac Operon into two parts for easy understanding.
Switch off condition- when lactose sugar is absent in the cell and
switch on condition- when lactose sugar is present in the cell.
Switch off Condition
When lactose sugar is present in the cell
First, the transcription of the regulator gene produces the repressor m-RNA, which is then translated to form the repressor protein.
Now if the lactose sugar is absent in the cell, the repressor protein binds to the operator gene in the absence of lactose.
Due to which the operator gene becomes inactive, and there the switch off condition occurs.
Due to this, neither transcription nor translation takes place from the structural gene.
Due to which the synthesis of any kind of enzyme or protein does not take place from the structural gene.
Thus, if the lactose sugar is not present in the cell, the enzyme will not be formed from the structural gene.
Switch on Condition
Switch on condition when lactose sugar is present in the cell-
The whole process starts as similar to earlier, but this time lactose sugar is present in the cell
It binds with the repressor protein, and the repressor-inducer complex is formed. This repressor cannot be attached to the inducer complex operator gene.
Due to which the operator gene is activated, and there the switch on condition occurs.
By which the coding of enzymes or proteins starts from the structural gene, that is to say, m-RNA is formed from the structural gene after transcription.
This m-RNA is called lac m-RNA. Upon translation of the Lac m-RNA (m-RNA), beta galactosidase, permease and trans-acetylase enzymes are formed.
The beta galactosidase enzyme will break down the lactose sugar, forming glucose and galactose.
And the E.coli bacteria cell will meet its energy requirement from this.
In this post, we learned how gene regulation is a mechanism in E.coli bacteria, and the synthesis of the beta galactosidase enzyme is regulated by structural genes being coded for.
Overall, if the E.coli cell contains lactose sugar, the beta galactosidase enzyme will form and if the cell does not contain lactose sugar, then the beta galactosidase enzyme formation will also not take place.
(FAQ)Frequently Asked Questions
What is a regulator gene?
The regulator gene in the lac operon forms the inhibitor or repressor protein.
It inhibits the reduction of operon, thus controlling the negative of structural genes.
The structural gene is the main gene of the leukoperan, which is responsible for the formation of different enzymes.
What is an inducible operon?
The best example of an endurable operon is the lac operon, where lactose reduces the sugar inducer.
Who discovered lac operon?
Lac operon was discovered by Jacob and Monad in 1961
Which is the first operon to be discovered?
The lac operan is the first to be discovered
Is the lac operon a catabolic or anabolic operon?
The lac operon is the catabolic operon.
What is operator gene?
Operator gene, also called switch off and switch on gene, which controls the synthesis of m-RNA from structural genes.
This gene is turned off in the presence of the repressor protein or absence of lactose sugar, and turned on in the presence of the inducer or lactose sugar.
What is Promoter gene?
Promoter is the gene where the RNA polymerase enzyme binds, and starts the process of transcription that makes m-RNA.
What is a repressor?
Repressor is a protein that is translates from the regulator gene.
In the absence of the inducer or lactose sugar, repressor protein inhibits the formation of the protein.
Conclusion
If you have any suggestion or update of any kind and if you see any mistake then you must let us know.
We will do our best to update your suggestion or any mistake that happened anywhere in the post.
Thanks to you for giving your valuable time and if possible please share to others.
Good luck with your online journey.

