Biology is entirely based on Reproduction . Every living beings that we see we see around are product from reproduction . If i say this in short, reproduction is production of offspring in animals and plants as well as in all microbes. In this post we are going to learn what reproduction actually is .
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is a biological process in which new organisms produced from pre-existing parental organisms. Young ones or offspring’s grow & mature to repeat the same process.
Significance-
- It is the ultimate the process for continuity of species on Earth.
- It is the process to Sustain or Existence of Life on Earth
Main Features:
- In reproduction DNA replicates because its distributed equally in off springs.
- Reproduction also brings RNA, protein and other important biochemical synthesis.
- in addition the above cell division, growth as well as new reproductive cells forms.
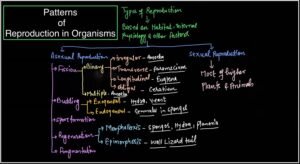
Types of Reproduction
It is based on the organisation of body of organisms, that is unicellular or multicellular or prokaryotic or eukaryotic or simple or complex.
Reproduction simply classified into two general types namely asexual & sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction-
When offspring produced from single parent with or without gamete formation called Asexual reproduction. such reproduction usually found in single celled organism with simple body organisation.
Common Features of Asexual reproduction:
1.Uniparental that is single parent is involved in most of cases it is the female parents or sex is not specified such as in Amoeba, Bacteria, Protista, Monera, Fungi, Algae or other Unicellular Organism.
2.Clone formation take place(described later).
3.No variations coming due to absence of meiosis cell division.
4.No fertilization or syngamy, it means there is no fusion of two opposite gametes(male gamete-sperms or female gamete-ovum).
5.No evolution, hence not favors in adaptation in changeable environments. 6.Gamete may or may not produced, like in case of parthenogenesis.
7.Cell division is mitosis for new individual formation.
8.Fast process, hence may crowding take place & their may be chance of pressure on natural resources as well as intraspecific competition.
Clone-
Those individual organisms which are morphologically and genetically similar to their parental organisms that is exact identical copy of their parental organism.
Types of Asexual Reproduction- It is of following types in diverse organisms.
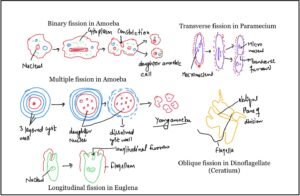
Fission-
In this single cell organism divides into two daughters cells.it may be binary fission or multiple fission (as in Plasmodium, Amoeba).
Binary fission further classified in to different types on the basis of plane of division of organisms body, hence it may be Longitudinal(Euglena), Transverse(Paramecium), Oblique(Dinoflagellate-Ceratium) and Irregular or Simple type(Amoeba).
Budding-
Bud is tiny outgrowth develop in/on the body of parent and after matured detached from parent body and ultimately develop into new individual. Such as in Yeast, Sycon, Hydra. Normally most of in these cases buds are exogenous that is develop on the surface of body or externally.
Budding may be endogenous as in the Gemmule formation in fresh water Sponges.in sponges buds formation take place in side the body or internally.
Fragmentation-
In this parent body break into small pieces and from each piece new individual id develop. such pattern of reproduction found in the Sponges, Sea Anemones, Echinoderms(Starfish), Filamentous Algae(Spirogyra), Fungi(Rhizopus), Bryophytes(Riccia, Marchantia) Pteridophytes(as in Selaginella)
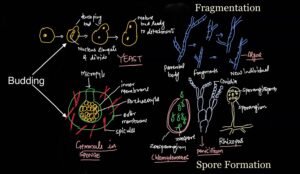
Spore Formation-
Spores are the simple thin or thick wall structure develop in sporangium or fruiting bodies after mitosis division, hence also called Mitospores and under favorable conditions on germination produced new individual organisms. Spore formation common in Monerans, Protistans, Fungi and in Algae.
Spores formation also take place in sexual reproduction but please not confused because in sexual reproduction spore form after the meiosis cell division, hence also called Meiospores.
Regeneration-
In this the accidentally break part of individual develop into whole organisms(as in Hydra ,Sponges) or only lost part is regenerated as in Lizard(Tail regeneration) and Salamander(Limb regeneration). if whole body is develops from a small piece then it is said to be Morphallaxis or if only lost part regenerated then it is said to be Epimorphosis.
In Lizard, it has been seen that if tail is lost accidentally then only tail is regenerated at the the point of tail area not else where and the lost tail is not develop into new individual, Similarly in Salamander, if Limb is cut then only limb regeneration take place.
Soon in next post we shall Learn about Sexual Reproduction
Thanks 😊😊

