Welcome to kashibiology.com
In this post we shall understand about about the basic introduction about the sexual reproduction, origin of sexual reproduction as well as some important terms for academic and medical competitive examination point of view.
Reproduction in Organisms class notes NCERT part one
Sexual Reproduction
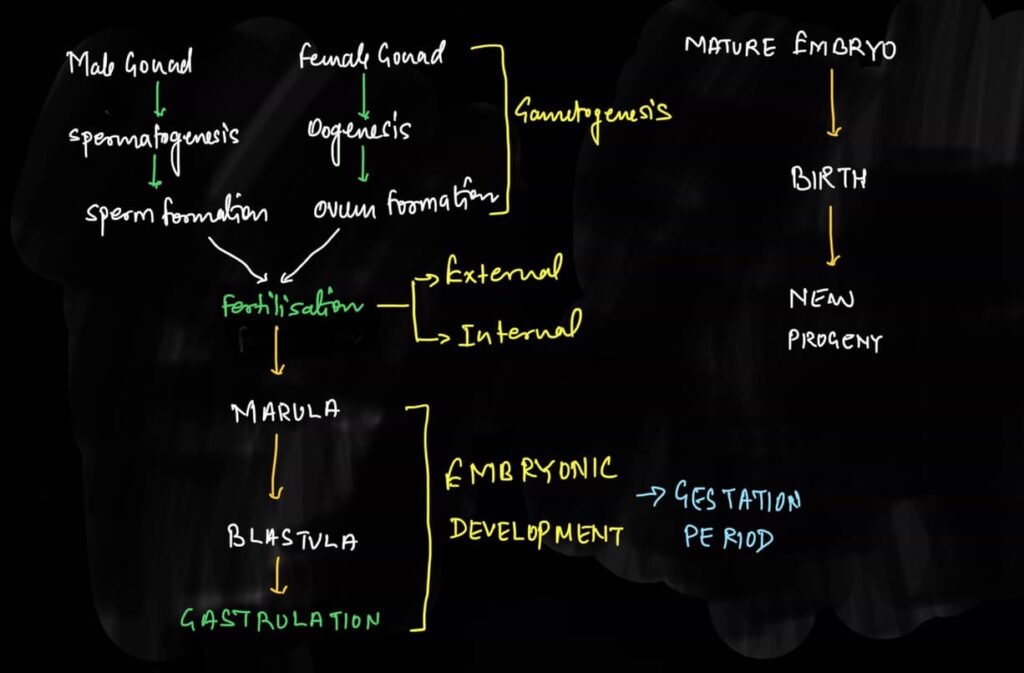
Sexual reproduction is the process in which gamete formation as well as fusion of gametes takes place.
The process of sexual production involve following steps which are categorized into three categories-
Namely-
- Pre fertilization events
- Fertilization events
- Post fertilization events
Pre fertilization events
In pre fertilization events gametogenesis and gamete transfer take place.
Gametogenesis
In the process of gametogenesis male and female gametes form in testis & ovary respectively.
Male gametes are called sperm which develop in testis while the female gametes are called ovum, which develop in ovary.
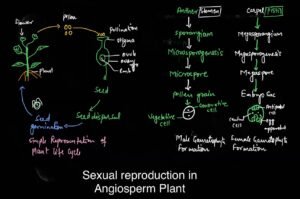
In the case of flowering plants (Angiosperms) both male and female reproductive organs are found in flowers.
Male reproductive organ is called stamen and the female reproductive organ is called carpel or pistil.
In plants, male gametophyte is called pollen, which produces male gamete while the female gametophyte is called embryo sac in which egg is present.
Gametes Transfer
It is related to the site of fertilization. If the fertilization is internal, then the male gamete transfers inside the female body, that is the female genital tract.
If the site of fertilization is external, then the transfer of gametes in the aquatic medium.
In this condition gametes release strong synchronization required for the success of fertilization.
In addition, in aquatic mediums large numbers of male gametes are required to increase the chances of fertilization.
In case of plant pollen grain transfer by the abiotic or biotic components to the stigma of carpel.
Fertilization events
Fertilization is the process in which male and female gametes fuse to form zygote.
It is a crucial event in all sexually reproducing organisms.
On the basis of site, fertilization is of two types
Internal fertilization
If the fertilization takes place inside the female body of genital tract then it is known as internal fertilization.
External fertilization
And if the fertilization takes place outside the body of the female usually in an aquatic medium then it is called external fertilization.
In vitro condition (artificial condition) fertilization can also achieve in a test tube for the test tube baby program.
Post fertilization events
It involves the zygote formation and development of zygote, that is embryogenesis.
Zygote
It is the unicellular structure which forms after the fertilization. in every sexually reproducing organism life begin from the zygote.
In case of algae and fungi zygote develops a thick wall that is resistant to desiccation and damage.
Zygote undergoes a period of rest before germination.
Embryogenesis
Development of zygote is known as embryogenesis and it is related to life cycle patterns of the Organisms.
It involves cell division and cell differentiation.
In plants after fertilization zygote develop into embryos, ovules develop into seeds and ovary develop into fruit.
In external fertilization embryogenesis takes place outside the body of the female parent.
While in internal fertilization embryogenesis takes place inside the body of the female parent.
Some important points
Origin of sexual reproduction
Sex originated in Protistan and algae. in Algae and fungi the reproduce sexually just before onset of adverse condition or unfavorable condition because I go develop help them to overcome the adverse condition in favorable condition the generally reproduce a sexually.
it is assume that gametes seems to starved asexual spores, which fuse to forms zygote. That has thick wall called zygospores and dispersed in surrounding environment and in favorable condition it will germinate to form new organism.
Earlier Sexual reproduction
Isogamous type of sexual reproduction is the most primitive type of pattern.
Later it became an isogamous and oogamous type.
Sex organ evolved and differentiated into male and female reproductive organs. It is due to the environmental and hormonal influences.
Types of sexual reproduction
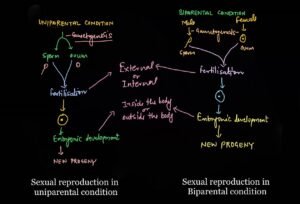
It is generally divided into two categories namely Syngamy and conjugation.
Syngamy is the fusion of two opposite gametes nuclei in order to make diploid zygote while conjugation is the primitive types of sexual reproduction in which two cells of opposite strain temporarily joint to each other by which genetic exchange take place between two cells.
Syngamy is further divided into two types on the basis of size of gametes and on the basis of sources of gametes.
On the basis of site of fusion or source of gametes
Endogamy (self fertilization)
In this gametes comes from the same parent
Uniparental type
Example Taenia, Earthworm
Exogamy (cross fertilization)
In this gametes come from two different parents.
Biparental pattern
Exogamy also found in bisexual animals and plants.
In bisexual animals and plants, it is due to different in times of formation as well as maturation of both the types of gametes or sex organ.
Such as-
Protoandry
It is the maturation of male reproductive system earlier than the female reproductive system.
Protogyny
It is the maturation of the female reproductive system earlier than male reproductive system.
On the basis of morphology and motility
Isogamy
It is a fusion of similar morphological male and female gametes. In this both male and female gametes are morphologically identical.
It is found in Chlamydomonas Algae.
Anisogamy
In this both male and female gametes differ in size but both are motile nature due to the presence of flagella.
It is also found in Chlamydomonas.
Oogamy
It is the most common type of sexual reproduction and commonly found in most of the sexually reproducing organism as well as in human.
In this male gamete is small and motile called sperm while the female gametes are large and non motile called egg or ovum.
Hologamy
In this process the whole body of the organism acts as a gamete and completely fuses to each other.
It is found in unicellular fungi Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae).
Monocarpic Plants
Plants which flowers once in their whole life cycle.
After flowering, they produce fruits and die.
Example-
All annual plants-like wheat and Rice
Biennial plants- like carrot and Radish
Polycarpic Plants
Plants which, Flowers in particular, season throughout the reproductive phase after flowers they do not die.
Most of the perennial plants are called polycarpic plants (or all the trees).
Such as- Mango and Guava etc.
Inter flowering phase-
The period between the two flowerings is known as interflowering or recovery phase.
Some of the perennial plants show unusual patterns of flowering.
For example-
In certain bamboo species plant, flowers once in its life cycle. that is after 50 to 100 years, then after producing flowers and fruits they die.
Another example is Strobilanthus kunthiana (common name Neelakurunji) which flowers once in every 12 years.
The color of flowers is purple-blue which attract the large number of tourists.
The Last time of flowering is September 2018. It grows in hilly areas of Kerala, Karnataka and Tamilnadu region.
Oviparous animals
Animals which lays fertilized or unfertilized called oviparous example reptiles birds
Viviparous animals
Animals which gives birth to young ones called viviparous
Such as- Most of the female mammals and human females.
Ovoviviparous animals
After fertilization embryos retain in the body but Placenta is absent and gives birth to young ones.
Example: Shark and rattlesnake.
Sexuality in organisms
In primitive organisms no differentiation of gametes occurs.
If gametes originated from same parent then it is called homothallic or bisexual condition.
If the gametes originated from different parents (male and female) then it is called heterothallic or unisexual condition.
When male and female flowers are present in the same plant then it is said to be monoecious condition.
Example- maize, coconut and Cucurbits
When male and female flowers are present on different plants then it is called dioecious condition.
Example- Date palm and Papaya.
Conclusion
Hope you will learn and understand the basic information about the sexual reproduction as well as some other important terms.
How do you like this blog, do give your opinion or any mistakes or updates in the comment box.
Thank you so much for giving your precious time