Welcome to kashibiology.com
In this post we shall understand about about the basic introduction about the vegetative propagation and its different types for academic and medical competitive examination point of view.
Vegetative Reproduction
It is the mode of asexual reproduction found in plants and many other lower organisms.
In this process a new plant arises or develops from vegetative units or vegetative propagules of the parent plant.
you may also like to read these notes-
Sexual Reproduction in Organisms class 12 notes NCERT
Asexual Reproduction in Organisms class 12 notes ncert
These vegetative units are the somatic part of a plant which may be derived from vegetative parts of plants such as- root, stem and leaves etc.
Vegetative propagation can be naturally found in plants or can be artificially induced by horticulture methods.
Vegetative or Somatic parts
Vegetative parts include all those parts of plants other than reproductive parts (that is flowers, stamen & carpel or pistil) such as- parts which are derived from the stem, roots and from the leaves etc.
These have the ability to give rise directly to new plant bodies under suitable conditions.
The types of propagules vary with the type of plants and species.
Advantages of vegetative propagation
- It is the fast process
- It preserves purity
- Provide resistance
- Good quality of races develop
- Clone formation occurs
Disadvantages
- Being asexual reproduction, vegetative propagation has same disadvantages or demerits.
- Features which is present in sexual reproduction are absent in asexual or vegetative propagation.
- Such as
- No variation due to the absence of meiosis cell division
- No adaptation
- No chance of evolution
A-Natural methods of vegetative propagation
Vegetative propagation by Root
Both tap root and adventitious root involve in vegetative propagation.
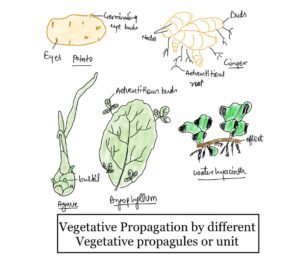
Tap root
In Dalbergia, Guava, Murraya adventitious buds develop from the taproot which later produces new plants.
Fleshy root
They also developed from adventitious buds, in case of sweet potato, dahlia and Asparagus.
Vegetative propagation by Stem
By aerial stem
Fleshy phylloclades and node in stem of sugarcane are also produces new plants after vegetative propagation.
By subaerial stem
Runners, stolans and offset are the structures arise from subaerial stem in different plants groups.
a.Runners
These are the horizontal branches develop from the base of root. Example Cynodon, Oxalis and Centella
b.Stolons
These are the arched branches. Example Strawberry and Vallisneria
c.Offset
These are the long runners in some aquatic plants. Example Eichhornia (water hyacinth/terror of Bengal) and Pistia.
By underground stem
Tubers, Bulbs, corms and rhizomes and suckers are the vegetative propagules arise from the underground stem in different plant species.
a.Tubers
They are the underground stem which bears buds over the nodes. Later buds develop into new plants.
Example- in potato
b.Bulbs
They are the underground condensed shoot with one or more buds present inside the bulbs, which form new plants.
Example- in Garlic and Onion etc.
c.Corms
Unbranched swollen underground stem has circular nodes which has buds. Later these buds form new plants
Example- Zamikand and Colocassia
d.Rhizomes
The main underground stem has buds for new shoot formation.
Example- Banana, Ginger and Turmeric
e.Suckers
These are the slender underground branches developed from the base of aerial shoot.
Later they grow for some distance and form new plants.
Example- pudina or mint and the Chrysanthemum
Vegetative propagation by leaves
Adventitious buds in Leaves
These adventitious buds develop at the marginal notches of leaves which later develop into new plants.
For example- in Bryophyllum and Adiantum (walking fern)
Bulbils
In agave they are the modified floral buds develop on flowering axis.
In the case of oxalis, agave and pineapple multicellular fleshy buds are found which help in the new plant formation.
Turions
They are the swollen buds detach from parent plant, mostly found in aquatic plants.
These buds are inactive in winter but active in spring.
For example- Utricularia and Potamogeton
B-Artificial methods of vegetative propagation
It is also known as the horticulture method used by gardeners.
In this process the desired plants (mostly for flowering and fruiting plants) propagated by various types of methods.
Such as- cutting, layering, grafting and micro-propagation.
Cutting
In this process the vegetative part of the plant such as leaf, root or stem cut and then dipped in appropriate growth media.
Later, this produces a new plant,
- Leaf cutting has been done in Sansevieria
- Stem cutting has been done in Lemon and China rose etc.
- Root cutting has been done in BlackBerry and Raspberry etc.
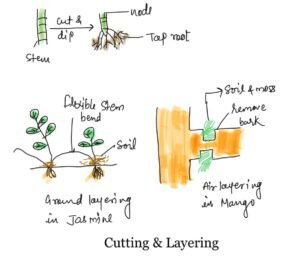
Layering
It is of two types namely ground layering and air layering.
Ground layering also called Goatee which is used in case of flexible stem while the air layering used in case of solid stem.
In layering process, removing the outer dead part of stem or bark then covered with soil and mosses which hold moist.
Ground layering
In this the flexible stem layered or cover by soil.
Later a new branch developed from the ground layer.
Example- in Jasmine plant
Air layering
In this the upper part of solid stem remove without damaging of vascular tissues then after this moist soil and moss has applied.
It has been done in mango, lichi pomegranate plants.
Grafting
It is the process of combining the character of two different species.
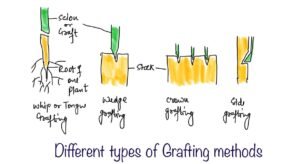
The part of the plant which is grafted is called scion or graft and part of plant (any branch or root or stem) where scion or graft is attached is called stock.
It is of different types namely
- Whip or tongue grafting
- Wedge grafting
- Crown grafting
- Side grafting
- Bud grafting
In bud grafting, bark and cambium used. The method of bud grafting has been used in apple, rose and peach plant
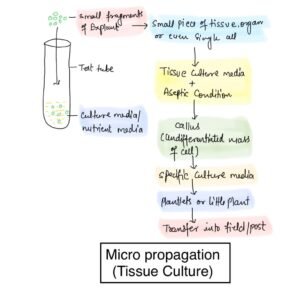
Micropropagation (Tissue culture)
It is the method used to grow a plant by using its reproductive or non-reproductive parts.
The term Micropropagation is frequently used, due to a small part of the plant being used in this method.
The small part is called explants, which is a small piece of leaf, tissue, organ or even single cell.
Then it grows in appropriate culture media under aseptic conditions.
In culture media explants start dividing in suitable condition and produce undifferentiated mass of cell called callus.
Then callus is cultured in a specific growth medium which ultimately produces plantlets or little plants.
Advantage of Micropropagation
- A small part can be used to produce a large number of plants.
- Rapid reproduction
- Identical offspring form
- Desire feature can be preserved
- Micropropagation is faster and easier
- Less expensive
- Ornamental and fruit trees multiply rapidly.
Conclusion
Hope you will learn and understand about the vegetative propagation, its different types as well as merits and demerits.
How do you like this blog, do give your opinion or if any mistakes (in the post) or updates in the comment box.
Thank you so much for giving your precious time
