In my previous post i have explained the basic terms we need to learn before understanding the full concept of Biotechnology . If you haven’t read the basic terms of Biotechnology you can read here .
In this article we are going to read everything about biotechnology like What is Biotechnology , what are it’s principles and importance of enzymes in Biotechnology .
Biotechnology:Definition:Principles & Important Enzymes
Biotechnology can be defined as Using of living organisms or their components or enzymes to produce products & processes for Human welfare.
According to European Federation of Biotechnology (EFB)-
It is the integrated use of Biochemistry, Microbiology, Engineering Sciences and Natural Sciences, in order to achieve technological (Industrial) application of the capabilities of Microorganisms (MO), cultured tissues & parts thereof.
Principles of Biotechnology
There are two main principles of Biotechnology
Genetic Engineering(r-DNA technology)–this includes
Gene cloning
Gene transfer
Alter the nature of Genetic Material
Bioprocess (Chemical) Engineering-Which include
Maintenance of sterile Microbial culture/cell culture/ tissue culture Produce Biological products such as Vaccines, Hormones etc.
Down Stream processing
Tools & Techniques of Genetic engineering or r-DNA technology
Tools of Biotechnology(Genetic Engineering)-
Enzymes
Cloning Vectors
Competent Host Cell
Techniques of Genetic Engineering-
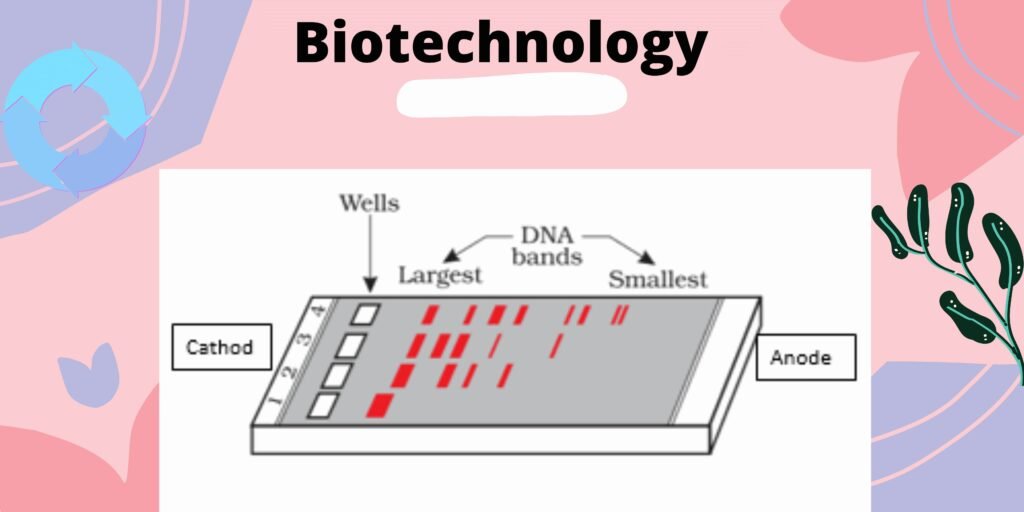
Gel Electrophoresis
PCR (polymerase chain Reaction)
Gene Transfer
Gene cloning
Southern Blotting
Western Blotting
Northern Blotting
Important Enzymes of genetic Engineering-
There are following types of enzymes which are used in genetic Engineering.
Need of enzymes related to type of cells which to be used for various purpose in r–DNA Technology.
Some common Enzymes which are frequently used are listed below
(i) Lysing Enzymes-These are used to open up cells to get their genetic Material or DNA (gene of Interest),by digesting Cell wall and Plasma membrane.
The choice of Lysing Enzymes further depend on the type of cell,
For example–
For plant cell–cell wall digesting enzymes–Cellulase,Pectinase
Plasma Membrane–Protease, Lipase
For Animal cell–Protease, Lipase–for Plasma membrane
For Fungal cell–Chitinase–For chitin Cell wall digestion.
Same Protease, Lipase– enzymes are used in Fungal plasma membrane digestion.
For Bacterial cell digestion–Bactericidal Enzyme–Lysozymes is used
(ii) Cleaving Enzymes (Nuclease)–These are Nucleic acid digesting enzymes which generally break the ester or phosphodiester bond between two adjacent nucleotides. For example
1-Exonucleases–It removes nucleotides from terminal ends either 5’ or 3’ of one of the two DNA – strands.
2-Endonucleases–Cleave at specific position within one strand of DNA except terminal end.
3-Restriction Endonucleases–break at specific position within both the strands of DNA Except terminal 5’ or 3’ end.
(iii) DNA Ligases–Used in joining two different nucleotides of DNA segments. Such as T4 – DNA Ligase.
(iv) Alkaline Phosphatase (AP)–Remove Phosphate (PO4) group from 5’ end of double/single stranded DNA as well as RNA.
Thus it cannot be ligated
(v) Phosphorylases–Just opposite Function of Alkaline Phosphatase(AP) i.e, add phosphate group (PO4) at 5’ end of DNA.
(vi) Synthesizing / Polymerising Enzymes–These Enzymes are used in Polymerisation or Synthesis of new Nucleic acid ether DNA or RNA.
(i) DNA Polymerase–Used in Synthesis of DNA
Discovered by A. Kornberg in E.coli (1956) hence also known as Kornberg Enzymes.
(ii) Taq-DNA Polymerase–Obtain from bacteria which is Thermostable Thermus aquaticus. Due to thermostable nature used in PCR.
(iii) Reverse Transcriptase–used in Synthesis of c-DNA or DNA from m-RNA.